Using shunts to spot PV module degradation
Scientists in Ireland investigated the effect of shunt resistance on a PV cell’s electrical performance. The group says its finding could potentially lead to the development of models for early detection of various forms of cell degradation, allowing for intervention to repair or replace components before major power losses occur.
Gallium doping and solar cell degradation
German scientists have conducted a series of experiments on gallium-doped silicon solar cells to understand the causes of degradation in PV cells and modules treated with gallium rather than boron. They confirmed that the performance losses are caused by a bulk defect in the material, and found that the right combination of light and temperature can “heal” earlier damage and even lead to small improvements in overall cell efficiency.
Damaging defects in silicon solar cells
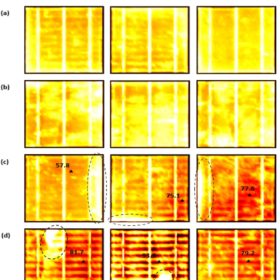
Scientists in the UK investigated the relationship between two of the most worrisome defects that can affect solar cells in the field – cracking and hotspots. Their work analyzed solar cells with different levels of cracking under varying light conditions, finding that the most severely cracked cells were considerably more likely to run at high temperatures and form damaging hotspots.
Keeping track of hydrogen for perovskite performance
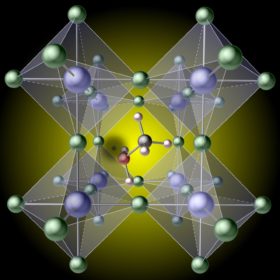
Scientists in the United States discovered that hydrogen plays a leading role in the formation of defects in a perovskite film, which limit their performance as PV devices. The discovery, according to the researchers, offers further insight into observations already established by trial and error and could help to push the impressive efficiency achievements already made by perovskites even higher.