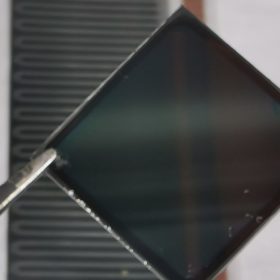
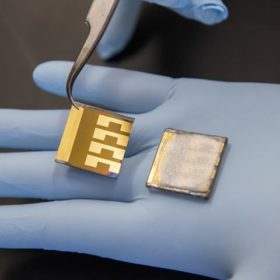
Focus on the negatives: A new path to highly efficient tandem cells
Scientists in the U.S. and South Korea have identified what could be a new route to high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells. Through engineering negatively charged particles in the passivation layer, the group made a tandem cell with 26.7% efficiency. With further tweaks to the silicon layer they expect to be able to surpass 30%.
Building on bifacial momentum
Getting the most out of a bifacial module requires a rethink at almost every level of system design and the industry is hungry for field data generated by such systems to better inform energy yield modeling and define the best approaches to maximizing yield at minimal cost. In May, the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory began a three-year study into bifacial performance which is beginning to yield results.
International consortium claims 25% efficiency for perovskite CIGS solar cell
Researchers led by Belgian institute imec claim to have achieved the result with a 1cm² perovskite tandem solar cell. The result tops the 24.6% efficiency the consortium announced in September 2018. The cell’s developers are now aiming for 30%.
Preventing lead leakage in perovskite cells
A U.S. research group has used a lead-absorbing material to coat the front and rear of a perovskite solar cell stack. The researchers claim the films captured 96% of lead leakage when the cells were damaged.
A quantum dot solar cell with 16.6% efficiency
Scientists at Australia’s University of Queensland have set a new world efficiency record for a quantum dot solar cell. The group fabricated a 0.1cm² device from a perovskite material and measured power conversion efficiency at 16.6%. The record has been verified by the United States National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
Innovative PV modules at Intersolar San Diego
In sunny San Diego for Intersolar 2020, we’re seeing a new idea for tracking rooftop solar modules, diodes moving to cell level, two types of building-integrated solar products and some solar hot water.
MIT researchers put slimmer silicon back on the table
With solar grade polysilicon prices having plummeted in recent years, cutting down on consumption of the material has not been a priority. But strategies exist and significant savings can be made through deploying thinner wafers that use less silicon, insists a new paper published by MIT and NREL. And as manufacturers are increasingly hitting dead ends on other routes to cost reduction, this option could be back on the table for many.
US scientists claim clear-sky irradiance model provides better results for module testing
Researchers at the American Institute of Physics have used the clear-sky irradiance model developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory to measure the degradation rates of solar panels at a testing field in Germany over five years. The scientists say the model, when combined with real-world data, offers an efficient tool to evaluate the aging of PV technology.
U.S. research teams aim for long-duration storage at $0.05/kWh
To get long-duration storage costs down to $0.05/kWh, research teams funded by ARPA-E are pursuing breakthroughs in flow batteries, hydrogen storage and other technologies – even thermovoltaics.
Aquavoltaic potential in Taiwan
Scientists have developed a new mathematical model which indicates floating solar on fish farms could be a lucrative option in land-scarce Taiwan. Although floating arrays could hinder fish production, the losses would be largely compensated by electricity-related income.