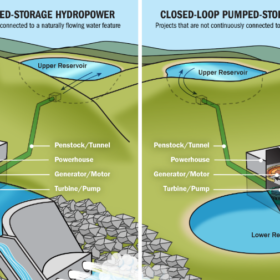
Closed-loop pumped hydro on the rise
Closed-loop pumped-hydro storage offers more chances to minimize environmental effects on water sources and overcomes the problem of finding suitable sites. According to an Australian research team, closed-loop systems could prevail on open-loop systems in the future and this trend is confirmed by another group of scientists from the United States.
Canal in Spain may host 160 MW solar plant
The government of Spain’s Navarra region has approved a 160 MW solar project planned by the local renewable energy association Anpier. The plant is to be deployed on the Canal of Navarra, which is one of the country’s largest artificial irrigation canals.
Indonesia moves forward with 1 GW pumped storage hydropower plant
The World Bank has agreed to finance part of a project owned by Indonesian state-owned utility, PLN. The facility is planned to enable a larger penetration of renewable energy to provide with power two large demand centers in West Java.
The world’s first large scale hybrid hydro-floating solar power plant
A Norwegian consortium led by Scatec is planning to build a hybrid hydropower-floating PV plant at an unspecified location in West Africa. Building both facilities simultaneously will help its developers define a series of parameters for proper sizing, optimization and design, and set a benchmark for future projects of this kind.
Combining big floating solar with hydropower
Scientists in Bangladesh have evaluated how a 50 MW floating PV plant could be integrated with the 230 MW Karnafuli Hydroelectric Power Station, located at the Kaptai Dam on the Karnaphuli River. They found that the two energy sources can be perfectly optimized and that PV can compensate for the reservoir’s shortage of water storage during the winter season while hydropower can compensate for the poor yields of the floating array during the monsoon season.
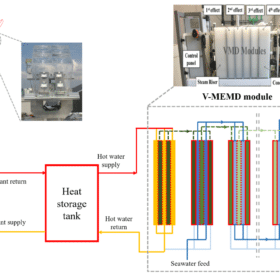
Rooftop CPV-thermal tech to produce electricity and freshwater
It’s claimed the decentralized desalination system can deliver a levelized cost for desalinated water of US$0.7-4.3/m3, depending on PV costs and electricity prices. It was built with several concentrated photovoltaic/thermal (CPV-T) collectors, a hot water tank, a V-MEMD module, a seawater feed tank, and a distillate tank.
Chilean startup using PV to produce potable water from humidity
A Chilean startup is using solar energy to produce high-quality drinking water from the humidity in the air. The first plant is located in Chile, but there are plans in the works to expand to Colombia and Peru.
How much floating PV is enough?
Scientists in the UK have had a closer look at the impacts of floating PV systems on the water. They found that their cooling effect on water mitigates blooms of toxic blue-green algae and increased water evaporation, which are both caused by global warming. They also warned, however, that colder water may result in a reduction of the duration of so-called thermal stratification. The right proportion between the surface occupied by the PV array and a water surface’s total area is key for addressing this issue.
Solar canals already competitive with ground-mounted PV
U.S. researchers have assessed the technical and economic feasibility of solar canals in California and have found that their LCOE is already close to that of ground-mounted solar plants. Three different project configurations were analyzed for eight different sites across the California network of canals.
Hydro-PV microgrid in Patagonia
In a national park in Chile, a hydropower plant has been combined with a solar system and battery storage to replace diesel generation.