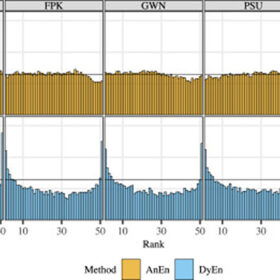
Ensemble techniques for solar energy forecasts
A Chinese research group has sought to understand the relative performance of two weather prediction techniques based on ensemble modeling for solar energy forecasts. The scientists applied the two methods in combination with three classical post-processing methods.
Has the US caught up with European agrivoltaic deployment?
With so much more agricultural real estate than Europe, the United States is building on the body of research built up across The Pond and rolling out solar panels on farmland at an impressive rate.
US developer secures $779 million for massive 800 MW solar project in Illinois
Swift Current Energy has secured $779 million in financing for an 800 MW solar project in Illinois – the second-largest PV installation in the nation.
A simple way to bring solar to multi-family apartments
Offering solar savings to apartment dwellers, and particularly renters, is not a simple task – as low take-up in Germany has demonstrated. Mel Bergsneider, from Australian startup Allume Energy, explains how a product offered by her company could change all that.
Weekend Read: Much more than Goodenough
The world would have been a different place today had John Goodenough accepted the Shah of Iran’s $7 million offer, in 1974, to carry out solar research. Instead, he secured a job as the head of inorganic chemistry at the University of Oxford. During his tenure, he made a lithium-ion battery discovery that would affect the lives of almost everyone.
The problem with aqueous zinc batteries
US scientists studied a zinc-manganese dioxide battery and found that hydrogen, rather than zinc-ions, move back into the manganese cathode, damaging its structure. The researchers will be able to use this knowledge to pursue new ways to improve its performance.
Covid-19 weekly round-up: It is still unclear how the crisis will play out on various solar segments, although one US installer says business has never been better…
Module price falls driven by the energy demand slump and Chinese oversupply may reverse at the end of the year, Germany appears immune to the Covid rooftop curse and emergency funding has been offered up to EU businesses affected by the crisis.
Improving magnesium-based batteries with chaos
Researchers have found strong anodic activity in disordered particles of magnesium chromium oxide. Unlike conventional, ordered nanocrystals, the disordered particles reportedly achieved reversible magnesium extraction and insertion.
The year in solar, part IV: More storage and hydrogen advances as solar just kept getting cheaper
Battery innovations started to come thick and fast this quarter as the hunt for alternatives to lithium-ion intensified and the latest slew of solar tenders indicated the relentless pressure on solar power generation costs was showing no sign of abating.
Amazon to build 149 MW solar plant in Spain
The solar project, southeast of Seville, will power Amazon Web Services data centers and logistics locations, and is expected to start generating next year. The company has launched its Climate Pledge with the aim of complying with the Paris Agreement 10 years early by neutralizing carbon emissions by 2040, and of operating with 80% renewable energy by 2024 and 100% renewable energy by 2030.