The Hydrogen Stream: Ukraine invasion raises price of gas-powered grey ammonia
With fears over Europe’s gas supply tightening, the Australian government is forging ahead in the green hydrogen sector by launching tech incubator HyGate and awarding Volt Advisory Group cash to develop a renewable energy microgrid. Australian business Fortescue Future Industries and Europe’s Airbus will work on hydrogen-powered aircraft and Kawasaki Heavy Industries is making strides in transporting hydrogen from the state of Victoria.
The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen-fuelled V8 engine for automobiles from Toyota, Yamaha
In other news, Belgian company Tree Energy Solutions (TES) is accelerating plans to develop the German port of Wilhelmshaven into a “world-scale” hub for importing green gas, and German engineering company MAN Energy Solutions will invest up to €500 million in its hydrogen-focused subsidiary H-TEC Systems.
The Hydrogen Stream: World’s largest electrolyzer fab breaks ground in Australia
Fortescue Future Industries says the first electrolyzers to be manufactured at the facility, early next year, are earmarked for use in Queensland at FFI’s planned green-hydrogen-to-ammonia project on Gibson Island.
The Hydrogen Stream: Airbus plans flight test with direct combustion engine fueled by hydrogen
Elsewhere, Chinese researchers have synthesized ultrafine Pd100-xCux nanodot-modified TiO2 photocatalysts that display optimized energy barrier for interfacial hydrogen desertion, which reportedly exhibits excellent H2-evolution activity and stability, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has presented its plans to establish the Takasago Hydrogen Park, calling it the world’s first center for validation of hydrogen-related technologies, from hydrogen production to power generation.
The Hydrogen Stream: CPV-powered PEM electrolyzers for 1.2MW demo in Portugal
Fusion Fuel Green has developed a small PEM electrolyzer that will be used in a green hydrogen project in Iberia. Elsewhere, India’s Adani Group and Canada-based PEM fuel cell producer Ballard Power Systems have signed a memorandum of understanding to evaluate a joint investment in the commercialization of hydrogen fuel cells for mobility and industrial applications in India.
The Hydrogen Stream: Europe’s largest green hydrogen project takes shape
Production for the HyDeal project is planned to start in 2025; the total installed capacity is expected to reach 9.5 GW of solar power and 7.4 GW of electrolyzers by 2030. Elsewhere in the world, India and Brazil are preparing rules and laws to promote green hydrogen, while research activities continue to increase hydrogen fuel cell’s efficiency and hydrogen’s use in the aviation sector.
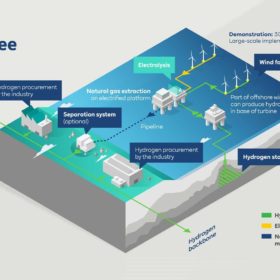
The Hydrogen Stream: Offshore green hydrogen project in the Dutch North Sea
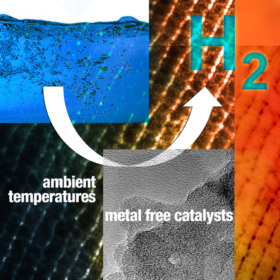
As research into non-rare metal catalysts continues, companies in northwest Europe are working on an offshore green hydrogen demonstration project, the first European data center to run on green hydrogen, and on hydrogen-based solutions for container transport. Meanwhile, European institutions are prepping for stronger hydrogen collaboration with Africa.
The Hydrogen Stream: New dehydrogenation process to improve hydrogen storage
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Ames Laboratory launched a new catalyst based on nitrogen and carbon to extract hydrogen from hydrogen storage materials at mild temperatures and under normal atmospheric conditions. Furthermore, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa said that the country is working on attracting new investments in electric vehicles and hydrogen and Norwegian consultancy and classification society DNV launched, together with 18 industry partners, a new Joint Industry Project (JIP) to enhance the standardization for hydrogen production systems that use renewable energy-powered electrolysis to produce green hydrogen.
Italy’s third Capacity Market auction expected to open new opportunities for large-scale storage
The retirement of coal baseload capacity, some regulatory adjustments and high energy prices volatility could bode well for the deployment of batteries in Italy, and especially in Sicily. Problems, mostly related to the timing and the structure of the auction, remain, however. We spoke about it with Michele Scolaro, Aurora Energy Research Associate.
The Hydrogen Stream: Fortescue develops tech based on photocatalytic water splitting coupled with solar
Australia’s Fortescue Future Industries wants to develop a green hydrogen technology based on photocatalytic water splitting coupled with solar radiation. Elsewhere, Linde has signed a long-term agreement with German chemical company BASF for the supply of hydrogen and steam in France and Nel has received a contract for a containerized PEM electrolyzer and light-duty hydrogen fueling station package from an unnamed U.S. power utility.