Off-grid solar boosts income by 50% of household GDP in Africa – study
Gogla has released a report showing the positive economic effects of deploying small-scale pay-as-you-go solar systems in off-grid regions. More than half of the survey’srespondents reported having increased economic activity, with many of those starting new businesses or significantly increasing their household income.
UK calls for innovation in EV charging, $53 million for business development
Following the U.K. government’s announcement to significantly increase EV numbers on its roads, a call for applications was announced. Ramping up EV numbers does necessitate a convenient and low-cost charging infrastructure. To achieve this, public administration offices will fund trial phases of promising concepts. Businesses can apply until August 29.
Next Kraftwerke connects 2 MW battery to its VPP in Belgium
The virtual power plant (VPP) solutions provider connected its product with a 2 MW storage system in Belgium. It will be the country’s first storage system to take part in the grid’s frequency control reserve.
Veolia Foundation supporting a nano-grid project in Madagascar
The project connects four to six households, and lets dwellers pre-purchase daily access to electricity using a mobile app. A successful trial phase has just been finished and the executing association, Nanoé Développement has set new goals to reach in the near future.
BMW, Tesla open factories in China, driving EV market in spite of trade-dispute
In the wake of the U.S.-China trade dispute, the Chinese government has loosened its policy on ownership caps for factory sites for foreign car brands. Previously, car companies could only retain 50% of the ownership of a factory and had to set up a joint venture with a Chinese partner. By setting up shop in China, Tesla can avoid import duties on its cars, to cater to a broader customer base.
Ecoligo crowdinvestment campaign for flower farm PV system in Kenya launched
Ecoligo has launched another financing round for the installation of a rooftop solar PV system at a flower farm in Kenya. The system is set to reduce the farm’s grid electricity demand by 50%, and lower its OPEX.
Global EV market growing sturdily despite trade dispute setbacks
EnergyTrend recognizes recent tariffs developments will hit the electric vehicle (EV) industry. Despite this, environmental regulations, as well as costs and technological advancement, will prevail and continue to drive EV sales globally.
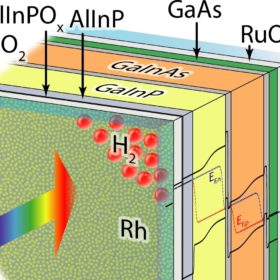
New solar water-splitting cell demonstrates 19.3% efficiency, increasing longevity significantly
The cell uses a novel approach that increases its conversion efficiency and longevity at the same time. Researchers claim it is a new world record for this type of application and highlight its importance in storing renewable energy in hydrogen to compensate for output and demand fluctuations.
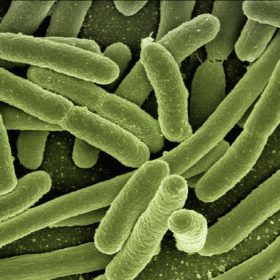
New bacteria-based solar cell doubles density, reduces production cost
Researchers coated bacteria with a semiconductor before application to an anode glass. This process is reportedly cheap and taps energy produced by the bacteria through photosynthesis. Additionally, the researchers state power output is not impeded by overcast skies, making it ideal for northern Europe, Canada, mines and other low-light environments.
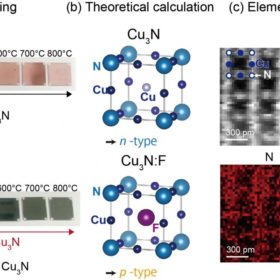
Replacement for CdTe: Copper-nitride conductor for thin film discovered
A novel method developed in Tokyo, Japan, allows a nitride crystal to grow, which can function as both an n- and p-type conductor. The material can replace cadmium-telluride (CdTe) in thin films, and make such solar cells more environmentally friendly, while enabling greater efficiencies, the researchers claim.