EU to gut the principle of sustainable taxonomy with inclusion of nuclear and gas
The EU’s Sustainable Taxonomy was intended to complement the Green Deal, provide investors with certainty about the sustainability of their investments, and help channel billions into sustainable, low-carbon processes and technologies. Despite input from experts and NGOs, the inclusion of gas and nuclear power just proposed by the Commission suggests that, once again, politics is trumping science.
Brazil heads for a solar installation rush
Brazil’s deployment of distributed generation PV (below 5 MWp) has exploded from a total capacity of 500 MW in 2018 to 7 GW by September of this year. The trigger for this increase, alongside rocketing electricity prices, was the 2019 proposal of law 5829, writes IHS Markit analyst Angel Antonio Cancino. The proposal is expected to pass into law at the end of this year and will gradually introduce grid-access charges for residential and commercial system owners.
A 200 GW solar year in 2022
Structural imbalances in the supply chain and the energy intensity and consumption controls that China imposed in late September have caused prices for most PV module materials and components to continue to rise. Shipping fees and PV plant construction costs also remain high. PV plants in many regions will therefore be postponed until next year, but it remains unclear when module prices will start to fall. Despite these challenges, the global race to cut carbon emissions continues, and InfoLink’s Corrine Lin forecasts a bright future for PV deployments in 2022.
Europe faces ‘new era of energy dependency’
The EU has been pouring money into European battery manufacturing and recycling projects but has, as yet, been unable to address the critical question of raw materials, according to analyst WoodMac.
2021 and beyond: European solar manufacturing must shine again
As 2021 ends, we enter a period of reflection and preparation. The ongoing pandemic has brought supply chain disruption, while the increasingly severe effects of the climate crisis loom over us. This winter, Europeans are struggling through unprecedented energy costs, driven by extremely high global gas prices. A year of difficulties has shown that Europe, more than ever, must accelerate the deployment of renewables to provide our economy with reliable, low-cost, and clean energy.
Record solar numbers expected this year but IEA highlights pricing concern
The Paris-based body expects the world will have installed almost 160 GW of solar this year, a record number, but still not enough to keep the prospect of a net zero global economy by mid century in sight.
COP26 and solar satellites for net-zero emissions
The United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) took place between October 31 and November 12 in Glasgow, Scotland, and ended with the adoption of the Glasgow Climate Pact by bringing 200 countries closer to keeping global temperature rise under 1.5°C by 2100.
Energy crisis and the energy transition
There’s a famous saying: “Never let a crisis go to waste.” The current energy crisis has had a terrible impact on many consumers, but it has also given the energy sector a golden opportunity to get in shape for the energy transition. Jon Slowe, the director of Delta-EE, examines the impacts and opportunities of the energy crisis currently playing out in Europe and what it could mean for the renewables sector.
Looking past PERC solar cells
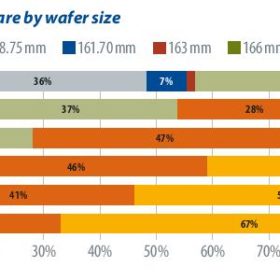
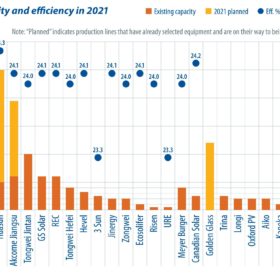
While the adoption of large-format wafers has driven a wave of capacity expansion for PERC, existing manufacturers and new entrants continue to evaluate TOPCon and HJT. An increasing number of HJT pilot lines and gigawatt-scale capacity expansion projects are appearing, as manufacturers see the advantages of fewer process steps, higher efficiency ratings, and better yield rates. The localization of equipment is also a driving factor. PV InfoLink’s Derek Zhao offers an update on the latest developments and process routes for HJT.
US solar market in flux
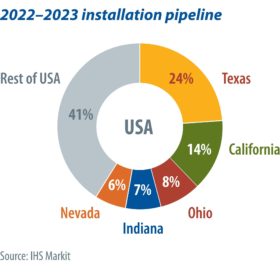
Next year will set new records for the U.S. solar market, with 30.4 GW of installations expected. The utility-scale PV pipeline in 2022 is nearly 50% greater than 2021 and 2023, due to the combined effects of pandemic-related supply chain impacts, the solar Investment Tax Credit schedule, and other module procurement challenges. Over the next two years, solar installations will be concentrated in Texas, California, Ohio, Indiana, and Nevada, with large portions of the pipeline being developed by a few key players in each state. IHS Markit’s Eric Wright takes a closer look.