Two-layer phase change materials for solar module cooling
Researchers in Iran have tested four different two-layer PCMs across several cooling system configurations and have found that the payback time of the proposed cooling tech is still far from reaching commercial viability. The system, however, was able to improve PV power generation by more than 3% and produce hot water with a temperature of up to 48 Celsius degrees from the solar module’s excess heat.
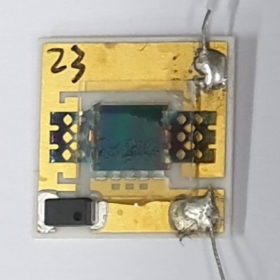
Multi-junction solar cell integrating radiative cooler
The triple-junction solar cell is based on indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and Germanium (Ge) and is made with a micro-grating made of glass, consisting of a two-dimensional x-framework structure fixed onto the surface of the solar cell. Its operating temperature was found to be 6 degrees Celsius lower than that of a reference cell without the cooling technique.
Multi-level fin heat sinks for solar module cooling
Developed by Malaysian scientists, the proposed multi-level aluminum fin heat sinks (MLFHS) were found able to reduce the module operating temperature by up to 8.45 degrees Celsius and increase power yield by up to 10.75%. The system cost was estimated at $0.60/W.
Spraying water system for solar module cooling
A British-Indian research group has developed an active cooling technique that is claimed to improve a PV system’s yield by around 0.5%. The system could be used in residential solar arrays and the water heated by the PV modules may be fed into a solar water heating system.
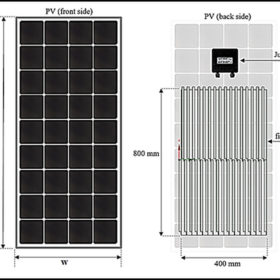
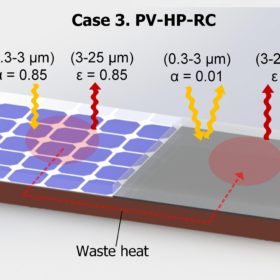
Lowering solar module temperatures with radiative cooling, heat pipes
Chinese scientists have developed a hybrid cooling technique to reduce module temperatures by up to 12.86 C and increase power yields by 7.25%. Their system features a PV module and a separate RC module, integrated with a flat plate heat pipe in between.
Cooling PV panels with water and cotton mesh
Scientists in Russia have developed an active cooling technique that spreads water on both sides of the module and uses a cotton wick mesh to absorb and spread the water that comes on the rear side. The system is able to reduce significantly a module’s operating temperature and lead to an overall improvement of 30.3% in its output power.
Cooling solar panels with thermoelectric modules
The cooling system was made with an aluminum heat sink and a thermoelectric module. The solar panel is cooled exclusively by the thermoelectric device, which is, in turn, cooled down by the heat sink via free convection. According to the scientists that developed the technique, it was able to reduce panel operating temperature by about 10 degrees Celsius.
Solar module cooling techniques for the desert
Saudi scientists have tested several cooling technologies for solar panels and have found that active techniques work better than passive ones under harsh climatic conditions. The most effective one consists of a system based on four heat pipes immersed in a box of liquid, as liquid bulk, integrated with the back of the solar panel.
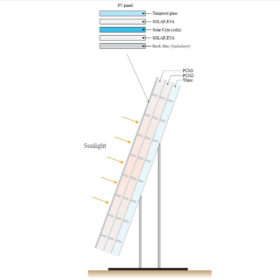
Solar module cooling technique based on multiple phase-change materials
Academics have utilized three PCMs, known as RT26, RT35, and RT42, and decided to pack them ascendingly depending on their melting points and heat-flow direction. The system is claimed to allow lower melting rates and longer thermal management of the modules.
Nano-micro-scale cooler for solar modules
The proposed technique is based on radiative cooling and consists of a glass coating made with a two-dimensional subwavelength nanostructured grating, which is imprinted in soda-lime glass and has enhanced mid-infrared emissivity, and a micro-structured grating. The temperature decrease provided by the nano-micro-grating coating was found to be approximately up to 5.8 degrees Celsius.