China’s PV capacity hits 364.4 GW
IEA-PVPS says that China added around 58 GW of new PV capacity in the first 10 months of the year, bringing cumulative installations to 364.44 GW. It says up to 100 GW of new capacity could be deployed by the end of this year.
The Hydrogen Stream: Green hydrogen via ammonia decomposition
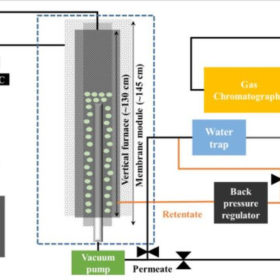
South Korean scientists have developed a highly selective palladium composite membrane on porous metal supports to cut the ammonia content of the permeated hydrogen stream. Dutch researchers, meanwhile, have presented two alternatives to this strategy – increasing the thickness of the membrane selective layer, or using a purification unit in the permeate of the membranes.
Floating solar cost-competitive with ground-mounted PV in southern Europe
Researchers have assessed the economic viability of utility-scale floating solar arrays in Europe and have determined that such projects are already cost-competitive in several southern European countries. They claim floating PV could become competitive across Europe if capital costs are reduced by 12%.
New manufacturing process for high-quality mono cast ingots
Chinese scientists have made mono cast silicon ingots with high purity and low manufacturing costs. The new method will help industrial casting manufacturers to improve the cost performance of casting ingots.
How variable is rooftop solar power?
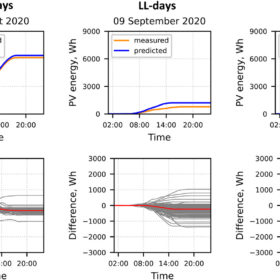
A research group has developed a new methodology that shows PV systems located in the same area could have similar distributions of power ramps. Their three-step method could be used for the dimensioning of rooftop arrays and the scheduling of daily operations.
Canada set to hit 5 GW milestone
Canada is set to install 500 MW of new solar in 2022, bringing its total capacity to about 5 GW, according to data from Canmet Energy. The country is expected to hit 35 GW of total solar capacity by 2050.
Scientists make first attempt to design solar cells based on kusachiite
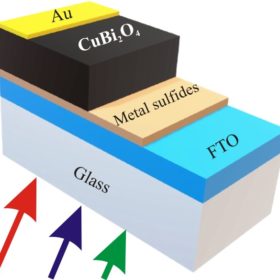
Indian scientists have designed a thin-film solar cell that uses a mineral made of binary copper(II) and bismuth(III) oxide. They identified a cell design with a tin sulfide buffer layer that offers efficiencies close to 27.7%.
Photovoltaics vs. concentrated solar power
Omani researchers have compared the performance of PV and concentrated solar power (CSP) in terms of energy generation intensity and the effective use of land at low latitudes near the Tropic of Cancer. They described nine project typologies and ranked them with three different simulation tools.
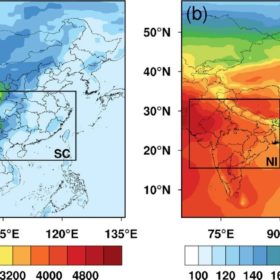
Impacts of clouds, aerosols on solar in China, India
Chinese researchers have modeled the impacts of clouds and aerosols on PV potential in southern China and northern India, which are similar in terms of latitude and elevation. They found that China offers lower PV potential due to a higher cloud effect.
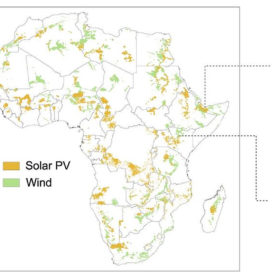
IRENA releases all-Africa dataset of locations for solar, wind
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) has published a dataset with 10,905 sites for PV deployment across Africa, with an estimated total capacity of 4.9 TW.