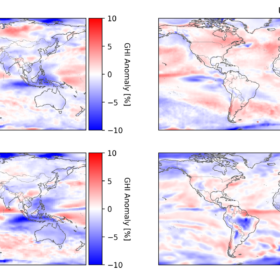
Forecasts predict strong solar performance for rest of 2025 in Europe, North America
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, forecasts that Europe and North America will benefit from relatively strong solar conditions in the second half of the year, while other major solar markets face more unfavourable trends.
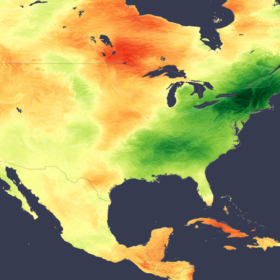
Hurricane, haze impact June’s solar production across Mexico, eastern U.S.
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that solar irradiance in June was impacted by Mexico’s earliest major hurricane on record, while wildfire smoke and persistent cloud suppressed irradiance over most of central and eastern U.S.
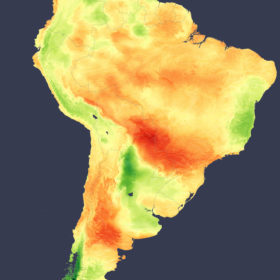
Shifting cloud patterns boost solar potential in the Amazon
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that solar irradiance levels across the Amazon Basin were 10% higher than the long-term average during April and May, reflecting a decadal trend towards drier conditions in the region.
East coast irradiance dips as storm systems dominate May
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that a low-pressure system over central North America in May suppressed solar irradiance on the East Coast while supporting moderate gains in the West and Midwest.
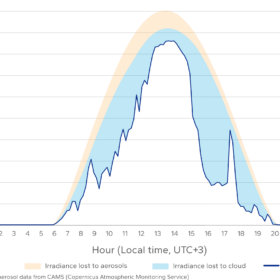
Dual aerosol events hit PV output across Southern Europe, North Africa
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that atmospheric particulates from both Saharan dust and Canadian wildfire led to reductions in solar irradiance and increased panel soiling in the Mediterranean region over the last week.
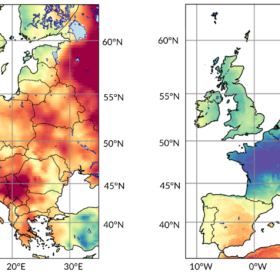
High pressure brings solar surge to northwestern Europe
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that solar irradiance in the British Isles reached up to 35% above the norm during the first half of May, while The Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany each recorded irradiance levels around 25% above average.
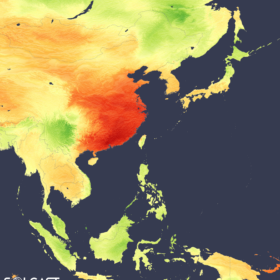
China’s year-to-date irradiance up 30% as aerosols drop
In another weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that a significant reduction in airborne pollutants has contributed to year-to-date irradiance in some parts of China being up to 30% higher than the long-term average. South Korea has benefited from a similar pattern, recording a 10% increase in irradiance from January to April relative to its long-term average.
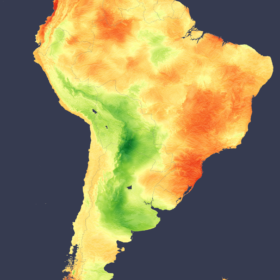
Solar gains across Brazil and Caribbean despite above average rain
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that Southern Brazil and the northern Andes were irradiance hotspots during March, posting anomalies as high as 30% above the climatological average. The increase came despite intense rainfall causing flooding in other parts of South America.
New WMO analysis underscores 2024’s solar anomalies
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, writes that while findings from the The European State of the Climate 2024 report align with its own solar analysis covering last year, differences in anomaly magnitude between the two datasets stem from the climatology periods used.
US South and Midwest enjoy up to 30% more irradiance in March
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that solar irradiance surged far above the March norm in the US South and Midwest, while parts of the US West and Canada were impacted by lower-than-average irradiance levels.