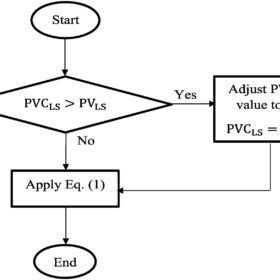
The PV cooler lifespan effectiveness factor
Researchers in Malaysia have defined a new parameter to evaluate solar module cooling techniques based on their lifespan effectiveness. They warned that the proposed methodology should be utilized only with standard test conditions, a temperature of 25 C, and a reference PV system without the cooling system.
Cooling down solar modules with cotton wicks immersed in water
The novel technique consists of attaching cotton wicks immersed in the water (CWIWs) to the backside photovoltaic module. The water is supplied to cotton wicks from top to bottom by gravity which the scientists said helps the effective absorption of cotton and reduces water consumption.
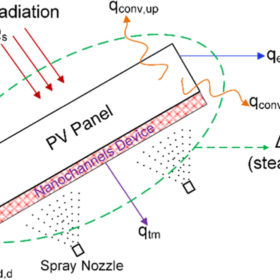
New solar module cooling tech based on porous nanochannels
US scientists have utilized a nanochannels device to cool down the operating temperature of a commercial PV module and have found that the proposed technique is able to improve power yield by up to 32.8%. Spray droplets are dispersed over the nanochannels device in order to eliminate the need for a continuous supply of a coolant.
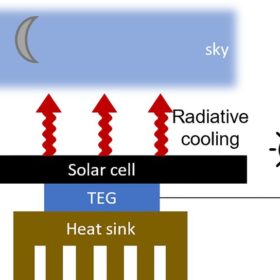
Radiative cooling-based solar cell with 50 mW/m2 of generation at night
Stanford University scientists have developed a solar cell with 24 hours of power generation via an embedded thermoelectric generator, which extracts power from the radiative cooler at night. Extra daytime power from excess heating comes from the cell itself.
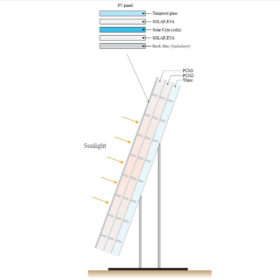
Two-layer phase change materials for solar module cooling
Researchers in Iran have tested four different two-layer PCMs across several cooling system configurations and have found that the payback time of the proposed cooling tech is still far from reaching commercial viability. The system, however, was able to improve PV power generation by more than 3% and produce hot water with a temperature of up to 48 Celsius degrees from the solar module’s excess heat.
Multi-junction solar cell integrating radiative cooler
The triple-junction solar cell is based on indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and Germanium (Ge) and is made with a micro-grating made of glass, consisting of a two-dimensional x-framework structure fixed onto the surface of the solar cell. Its operating temperature was found to be 6 degrees Celsius lower than that of a reference cell without the cooling technique.
Multi-level fin heat sinks for solar module cooling
Developed by Malaysian scientists, the proposed multi-level aluminum fin heat sinks (MLFHS) were found able to reduce the module operating temperature by up to 8.45 degrees Celsius and increase power yield by up to 10.75%. The system cost was estimated at $0.60/W.
PV module cooling techniques at a glance
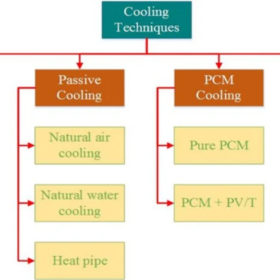
Egyptian researchers have analyzed all cooling techniques for solar module cooling. Their review includes passive and active cooling methods, cooling with phase change materials (PCMs), and cooling with PCM and other additives, such as nanoparticles or porous metal.
Spraying water system for solar module cooling
A British-Indian research group has developed an active cooling technique that is claimed to improve a PV system’s yield by around 0.5%. The system could be used in residential solar arrays and the water heated by the PV modules may be fed into a solar water heating system.
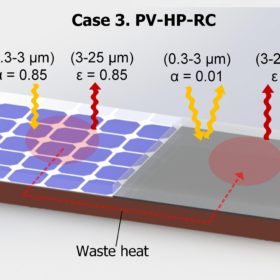
Lowering solar module temperatures with radiative cooling, heat pipes
Chinese scientists have developed a hybrid cooling technique to reduce module temperatures by up to 12.86 C and increase power yields by 7.25%. Their system features a PV module and a separate RC module, integrated with a flat plate heat pipe in between.