Using texturized glass in building-integrated photovoltaics
Researchers from Poland have assessed how texturized glass used as the front cover of building-integrated photovoltaic panels affects performance. They have found power yield could be up to 5% lower compared to modules based on conventional glass, with reflection parameters being up to 88% in visible region.
Solis introduces low-voltage hybrid inverters
The Chinese manufacturer said that its new series includes inverters with up to 15 kW of AC output. It supports a maximum input current of 20A.
Powering restaurants with rooftop PV, reversible fuel cells
Researchers have simulated the operation of bifacial PV and proton exchange membrane reversible fuel cells across restaurants in five different US states. Taking into account varying rates of bifacial PV’s rearside gains, they found that LCOE was as low as $0.029 per kWh.
Octaspherosilicates-based anti-icing coating for PV systems
Developed by scientists in Poland, the new coating uses transparent silicone-epoxy modified with functionalized octaspherosilicates. The researchers have created five samples, each with a different combination of chemicals, and have found that ice adhesion was reduced by up to 43%, with freezing delay time growing by up to 70 times.
Can Israeli PV tenders preserve competition in a concentrated market?
Researchers have studied Israel’s clearing price method for PV tenders and raised concerns about its potential for long-term dominance. They examined how power abuse and technological inefficiencies lead to market inefficiencies, concluding that a duopoly best suits the Israeli market.
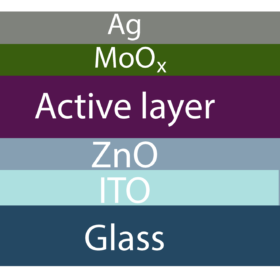
Organic PV module based on ultra-narrow interconnections achieves record-breaking efficiency of 16.1%
New research from China shows that ultra-narrow interconnections may considerably improve organic PV performance. The scientists built a 11.08 cm2 panel with an impressive geometric fill factor of 98%.
PV fault detection method based on deep learning of aerial images
Conceived an international research group, the proposed model uses the convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture U-Net for image segmentation and the the CNN architecture InceptionV3-Net for fault classification.
University of the Western Cape launches 4 MW solar, storage tender
South Africa’s University of the Western Cape (UWC) has opened a 4 MW solar and storage tender, with proposals to include a PV carport system and an online monitoring and management platform. The tender follows a build, operate, and transfer model for up to 20 years.
PV-driven lighting solution for rural areas
Scientists have created a lighting system based on the AEM10941 solar harvester developed by Belgium-based E-peas. The system is reportedly able to provide a full brightness run time of 10 hours.
SolarEdge unveils inverters for smaller solar projects
Israel-based inverter maker SolarEdge has unveiled its new TerraMax Inverter, which boasts 99% efficiency and enables 200% DC oversizing. It features an integrated night-time PID rectifier and is paired with the company’s H1300 Power Optimizers.