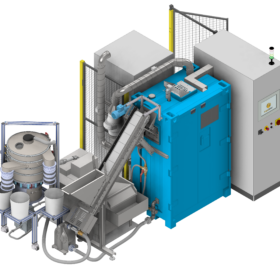
PV module recycling tech based on electrohydraulic shockwave fragmentation
An international research team has developed a new machine that utilizes shockwaves to separate the different materials of a PV module. Chemical processes can be further used to extract silicon and silver. Results show the recovery of more than 99.5% of the original weight of the panels.
Ecoflow launches 286 Wh portable power generator
The US-based company said its new River 3 Plus portable power station recharges from 0% to 100% in just one hour via AC outlet A version that includes wireless charging via an integrated 5,000 mAh power bank will be available later this year.
Experimental EV battery charges in 10 minutes in sub-zero temperatures
US scientists have developed a lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles that enables high range and fast charging in cold weather. The battery uses a single-ion conducting glassy solid electrolyte coating and does not require changes to chemistries or production processes.
PV-driven self-insulating composite exterior wall panel for building applications
Scientists in China have designed a solar self-insulated composite exterior wall panel, integrating a solar collector panel, PV panel, and insulation board. The proposed experimental setup has reportedly a static payback period of 1.1 years.
Six-year test field shows agrivoltaics can be critical for rice productivity
Scientists in Japan have conducted a field experiment in rice plantations hosting agrivoltaics systems and have found that rice growth can be affected by reduced biomass and reduced panicle number. However, their analysis has also shown that gross return in lowland rice agrivoltaics can be 14 times higher than rice growth without PV.
Using surplus solar power to pre-cool, pre-heat homes
Scientists in Australia have shown how pre-cooling and pre-heating could be implemented in Australian buildings with the support of excess solar power. Their analysis has demonstrated that summer has the highest potential for air conditioning demand reduction.
Japanese energy supplier to use green hydrogen for district heating, power
Akasaka Heating & Cooling Supply says it will use green hydrogen produced at an unspecified location in Japan to produce heat and electricity for its Akasaka 5-chome district heating system in central Tokyo.
Austa releases all-in-one storage system for residential use
Austa has launched an all-in-one residential storage system with a three-phase inverter offering output from 5,000 W to 15,000 W and storage capacities ranging from 10 kWh to 30 kWh.
Mibet launches new floaters for PV systems on deep water
Mibet has released new floaters for PV systems deployed in deep water. The G4M system, already installed in Indonesia on a body of water with a depth of 60 meters, allows the solar panels to be tilted at 5 degrees to 15 degrees.
Chinese scientists build polysulfide-iodide redox flow battery with 87.9% energy efficiency
Scientists in China designed a suplhuer-based redox flow battery with a peak power density of 95.7 mW cm2 and an average energy efficiency of 76.5% at 30 mA cm2 within 50 cycles.