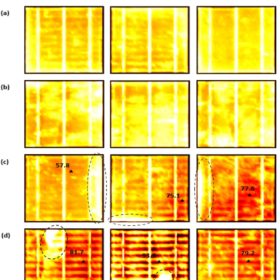
Damaging defects in silicon solar cells
Scientists in the UK investigated the relationship between two of the most worrisome defects that can affect solar cells in the field – cracking and hotspots. Their work analyzed solar cells with different levels of cracking under varying light conditions, finding that the most severely cracked cells were considerably more likely to run at high temperatures and form damaging hotspots.
Behind PID in bifacial solar cells
New research from Germany outlines mechanisms behind a form of potential-induced degradation specifically affecting the rear side of bifacial solar cells. Results suggest that the issue may be more complex than previously thought; and avoiding irreversible damage to cells in the field will require a rethink of testing standards.
Defining BIPV
Incorporating solar into our built environments represents an opportunity for hundreds of gigawatts to be installed worldwide without taking up any additional land. In many cases though, this will require solutions beyond typical rooftop PV installations and much closer cooperation between the PV and construction industries. A new report published by IEA PVPS looks to bring together the interests of both worlds, and clearly categorize both the building envelope and energy functions of different BIPV components.
Google lends a hand in the search for new solar cell designs with open-source tool
Scientists in the United States developed a computer simulator that can calculate the conversion efficiency of different solar cell materials and configurations – helping to guide research and optimization of new cell designs. The simulator is available to researchers as an open-source tool to save time and spot the best opportunities for optimization of any given approach.
Grid stability and 100% renewables
New research from Stanford University professor Mark Jacobson seeks to remove any doubts about grid stability in a world powered entirely by renewable energy. The latest study models 100% wind water and solar powered grids across the United States, finding no risk of blackouts in any region and also broad benefits in cost reduction, job creation and land use.
Ultra-thin silicon layers for 22.2%-efficient heterojunction solar cell
Scientists in the Netherlands fabricated a heterojunction solar cell with a layer of hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon just three nanometers thick. The cell’s efficiency was measured at 22.2%, below the highest achieved with HJT cells, however, the researchers note that successfully incorporating this material into the cell stack will open many new doors for improvement.
Fast charging for lithium-ion batteries needs a fix
Scientists in the United States placed fast charging for lithium-ion batteries under the microscope, finding that charging at higher rates can quickly damage the structure of a graphite anode, causing capacity loss even after a small number of cycles. By identifying the mechanisms causing this performance loss, the group can help point future research in the right direction.
Illustrating the n-type advantage
In a new white paper, Chinese PV manufacturer JinkoSolar demonstrates how its latest ‘Tiger Neo’ module, featuring the 182mm n-type TOPCon cells, achieves lower energy costs. Based on total project costs for various scenarios in China, the Middle East and Europe, Jinko calculates advantages arising from both the cell technology and its chosen wafer format.
Narrowing down a million molecules for the optimal flow battery
Scientists in the United States turned to artificial intelligence to speed up their search for new materials for use in a flow battery. The group developed a machine learning algorithm that could search a dataset of potential materials and identify those with the ideal balance of different characteristics that make it suitable for use in a flow batteries. The group says its algorithm could be applied to other battery technologies, and even in other fields.
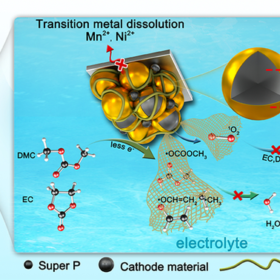
New ‘bioinspired’ solution to battery degradation
As part of their efforts to bring lithium-ion battery degradation under control, scientists in China have looked to emulate natural defenses many organisms have evolved to reduce oxidation reactions and related damage. With an additive that ‘scavenges’ reactive particles before they can contribute to degradation, the group was able to demonstrate significantly lower electrolyte decomposition in a working battery.