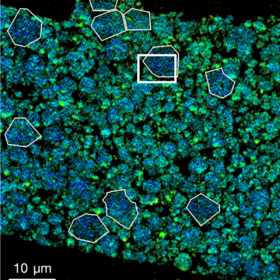
Zinc-iron redox flow battery with zero dendrite growth
Scientists in India fabricated a redox flow battery based on zinc and iron that showed strong storage characteristics and no signs of degradation over 30 charge-discharge cycles. The battery also showed no signs of dendrite formation, overcoming one of the key hurdles for redox-flow batteries based on these low-cost, abundant materials.
Cutting Europe‘s energy costs through interconnection
A new study from Stanford University professor Mark Jacobson models energy grids powered by 100% wind, water and sunlight across Western Europe. The study finds that in such a scenario, increased interconnection between countries would lead to lower energy costs and better grid stability, as well as a hedge against sudden loss of supply due to extreme weather or other events.
Hold your breath for a better battery
Recent research has revealed a previously underestimated role for oxygen in limiting the performance of lithium-ion batteries. Newly published research from both Japan and the United States has sought to look deeper into the chemical reactions at the heart of lithium-ion storage; and to better characterize the cumulative effects that minuscule amounts of oxygen released during these reactions can have on battery performance and safety.
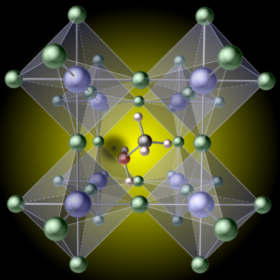
An environmental failsafe for lead-based perovskites
Scientists in Switzerland discovered that certain types of phosphate salt react with lead only in the presence of moisture, to form non-water-soluble phosphates. Incorporating these salts into the architecture of a lead-based perovskite solar cell could greatly reduce the risk of lead seeping into the environment should the cells be damaged, without incurring significant costs or negatively affecting the cell’s performance.
Supercomputer scientists dive deep into perovskites
Scientists in the U.S. used sophisticated computer modelling techniques to recreate the microscopic structures of a perovskite solar cell, revealing new information about defects within the materials that could greatly improved performance.
Two years of perovskite progress
Scientists in China examined some of the key achievements in the development of perovskite solar cells in 2020 and 2021. The group finds that translating laboratory achievements onto larger, manufacturable devices, is the biggest challenge, and sees continuing collaboration between the industry and academic researchers as the key to overcoming this challenge.
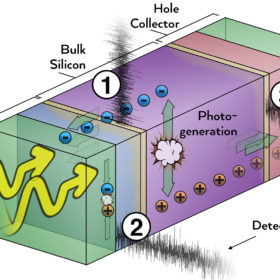
Bringing the noise for better solar cell efficiency
An international team of scientists developed a technique to isolate individual sources of electrical ‘noise’ within a solar cell. Comparing the technique to being able to pick out a single voice within a 200-person choir, they say the technique will help to improve understanding of where efficiency losses occur within a cell, and effective ways to mitigate them.
n-type perovskite tandem cell hits 27% efficiency
Scientists demonstrated a perovskite-silicon tandem cell that reached 27% conversion efficiency. Though higher tandem cell efficiencies have been achieved, this represents a big jump in efficiency for those utilizing n-i-p architecture, which previously had not surpassed 22%.
The weekend read: Looking at the energy transition’s bigger picture
Mark Jacobson, director of the atmosphere/energy program at Stanford University, has developed roadmaps for 143 countries to meet 100% of their energy demand from power generated by wind, water, and sunlight. In every case, these roadmaps promise major reductions in energy costs, while mitigating the effects of climate change and air pollution. pv magazine checked in with Jacobson for a look at the energy transition’s bigger picture.
Perovskites get a $14m boost
The United States Department of Energy is providing $14 million for a research center for perovskite solar technology. Led by Sandia National Laboratories, the center’s work will focus on establishing standard testing protocols as well as ensuring the long-term reliability of perovskite cells and the bankability of companies setting up to produce them.