The weekend read: Solar’s flexibility can be agriculture’s gain
Both solar and the farming industry are beginning to see potential in the combined use of land for food production and energy generation. And as innovators begin to experiment with different forms, it’s becoming clear that in most cases it is solar that will have to bend to the needs of agriculture, and not the other way around, to ensure a positive outcome.
New method to produce silicon anodes for lithium-ion batteries
Scientists in Sweden developed a new aerogel process to manufacture silicon anodes for lithium-ion batteries, promising to offer batteries with greatly increased capacity compared to those on sale today. By growing nanometer-sized particles of silicon onto graphite, the group was able to demonstrate a device that overcomes many of the challenges common to silicon as anode material. While there are still challenges in terms of stability and capacity retention, the approach could ultimately yield low-cost, large-scale production processes.
Quantum dot solar cells and the search for stability
In various forms, quantum dot technology has attracted plenty of attention among PV researchers recently. And as efficiencies have crept past the 15% mark, the community is beginning to look at other factors limiting the viability of quantum dot solar cells in a commercial setting. Scientists in Germany examined the degradation mechanisms affecting different quantum dot materials; and suggest a standardization of stability testing to enable comparability of results.
A 15.2%-efficient solar cell that you can fold in half
Scientists in South Korea developed a foldable thin-film device with some promising characteristics. Integrating a perovskite cell material and a carbon nanotube electrode, the group fabricated a device that achieved 15.2% efficiency and could withstand being folded more than 10,000 times at a bending radius of 0.5mm.
UK solar innovator planning unique thin film pilot
UK-based company Power Roll has picked up £5.8 million in investment over the past six months and plans to begin pilot production this year. The company has developed a unique flexible thin-film technology, which promises to combine both solar generation and storage.
Modeling the potential of lead-free perovskites
Scientists in India modeled the performance of tin-based perovskite (methylammonium tin triiodide) finding that with careful optimizations the material could achieve efficiencies beyond 28%.
From power to energy rating, for a better choice of PV module
A new report published by the International Energy Agency’s Photovoltaic Power Systems Program (IEA PVPS) outlines the need for PV module standards and testing to focus on ‘energy rating’ – an estimate of actual performance in a variety of climate conditions, rather than nominal power output or efficiency. The report finds that the IEC and other standards bodies are already beginning to make encouraging moves in this direction, but more work, and more data, are needed to make the most out of this approach.
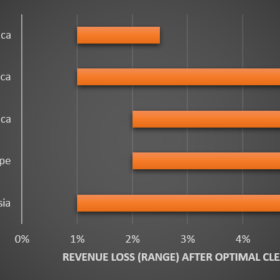
New model to predict PV module cleaning cycles and resulting profits
A group of scientists in Bangladesh has developed a model to determine the optimal cleaning schedule for a PV installation at any location in the globe, requiring only the average insolation and soiling rate for a given site to make the calculation. The study also draws new conclusions regarding the influence of sandstorms and rain on soiling, and aims to be among the first studies to paint a global picture of soiling trends by region.
Assessing the impact of large-wafer modules
Energy consultancy DNV GL has published new results comparing the performance of modules based on 166mm, 182mm and 210mm silicon cells. The assessment compares Trina Solar’s Vertex modules, which use the largest cell dimension, with unnamed competitors utilizing the other two sizes. Results from system simulations show a clear advantage for the two larger sizes, with 210mm edging ahead in terms of levelized cost of electricity.
A pinch of chili gives perovskites a kick
Scientists in China found that capsaicin, the natural compound responsible for a chili pepper’s spicy flavor, can also act as a ‘secret ingredient’ in perovskite solar cells, making them both more efficient and stable. The group added capsaicin to the precursor materials of a common perovskite, leading to dramatic improvements in the resulting solar cell.