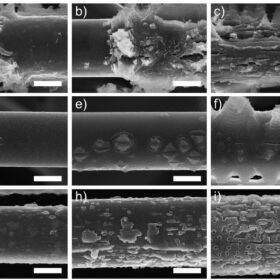
Paper-thin carbon fiber for battery with 428 Wh/kg energy density
South Korean scientists have developed a new way to integrate a lithium-metal anode into a battery and reach higher energy capacity levels than current lithium-ion tech. They worked with a carbon fiber paper infused with lithium and demonstrated an energy density of 428 Wh/kg, along with encouraging performance in stability and potential ease of manufacturing.
Silicon for batteries moves to commercial production
U.S. company Group14 Technologies today announced the launch of a factory capable of producing 120 tons per year of its innovative silicon-carbon-based anode material for lithium-ion batteries. The factory is located at Group14’s headquarters in Woodinville, Washington and is the first of several planned by the company.
Lithium metal enabler for low temperature batteries
Scientists in the United States demonstrated a new route to improving battery performance. The group integrated a self-assembling layer which forms on the surface of the anode, preventing the formation of dendrites. While their prototype has a very short lifetime, the group is convinced approach could lead to better performing batteries, and is particularly promising for low temperature applications.
An alumina lining for silicon in storage
Scientists at Rice University in the U.S. have conducted experiments with lithium-ion batteries using silicon as an anode material and made an unexpected discovery regarding an aluminum oxide passivation layer at the cathode. The finding could open up a new pathway toward better performing lithium-ion batteries.