The thermomechanical impact of plated copper contacts on heterojunction solar cells
UNSW researchers have found that annealing copper-plated contacts in heterojunction solar cells creates only localized stress. Their analysis also showed that, at typical annealing temperatures around 200 C, the probability of silicon fracture is very low.
New research sheds light on passivation-related defects in heterojunction solar cells
Korean researchers revealed that efficiency losses in heterojunction solar cells arise from two coexisting defect types – dangling bonds and weak silicon-silicon bonds. Their findings explain how hydrogenated amorphous silicon passivation help mitigate these defects and improve cell performance.
Longi unveils 34.58%-efficient tandem perovskite-silicon solar cell based on asymmetric self-assembled monolayer
In a new scientific paper published in nature, the Chinese manufacturer presented a new tandem perovskite-silicon solar cell based on a bottom cell with a heterojunction design. It also used a new type of self-assembled monolayer that reportedly reduces non-radiative recombination and increases cell efficiency.
New study confirms sensitivity of heterojunction solar cells to soldering flux
Researchers in South Korea have found that the contamination by small amounts of soldering flux residues during heterojunction PV module manufacturing can induce significant long-term performance degradation. Careful control of flux application methods and incorporating drying steps are proposed as potential solutions.
TU Delft researchers build 23.4%-efficient heterojunction solar cell with localized front contacts
Researchers at the Delft University of Technology have developed a top-down processing method localized the front contact in heterojunction solar cells. The new technique reportedly improves a cell’s short-circuit current density enabling higher power conversion efficiency.
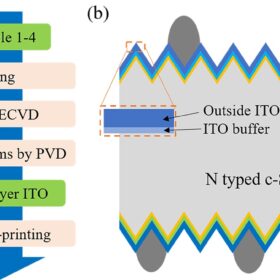
Heterojunction solar cell based on indium tin oxide buffer layer achieves 25.36% efficiency
Researchers in China have sought to increase the efficiency of heterojunction solar cell through a buffer layer made of indium tin oxide. This innovation reportedly resulted in a 0.1% efficiency increase deriving from optimized short-circuit current density and fill factor.
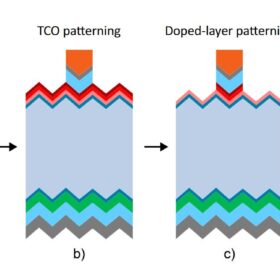
Dielectric capping layers improve heterojunction solar module reliability
A research group from France claims to have found a way to reduce indium consumption in heterojunction solar modules by 85 % while maintaining good performances and durability levels. The scientists tested different cell designs and the use of several capping layers to protect the cell from moisture degradation.
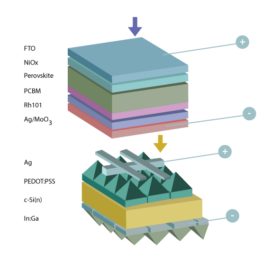
Indian scientists build 4T perovskite-silicon tandem cell based on hybrid heterojunction PV device
A research group in India has embedded a hybrid heterojunction solar cell as a bottom device in a four-terminal perovskite-silicon solar cell using a solution processing technique. The novel cell architecture, according to its creators, could be produced at significantly lower costs compared to conventional perovskite-silicon tandem designs.
Optimized gettering can improve heterojunction solar cell efficiency by 0.21%
Researchers in China have investigated the impact of phosphorus diffusion gettering on industrial silicon heterojunction solar cell and have found that, with an optimized gas flow, higher efficiencies can be achieved.
Trina Solar sets world record for solar module efficiency at 25.44%
Trina Solar has set a world record for solar module efficiency at 25.44%, verified independently by the CalLab at Fraunhofer ISE.