This August saw significant anomalies in solar irradiance levels across Europe compared to the long term average. Spain and the UK saw irradiance up by more than 10% due to a concentration of the jetstream towards Scandinavia, Central Europe and the Baltics, which received just 80% of average August irradiance according to data collected by Solcast, a DNV company, via the Solcast API.
The UK saw on average 110% of normal August irradiance, with values exceeding this in the north. Spain and Portugal received 10-20% more than normal, due to reduced cloud. The jetstream normally brings broad cloud cover across the continent, blanketing Europe from Spain, to the UK and extending south to Greece at this time of year. This August, the jetstream has been more concentrated, steering weather through the narrow gap between the UK and Spain, and pushing weather through to the rest of the continent, resulting in the irradiance pattern seen in the map below. Spain also saw other extreme conditions with wildfires throughout the month, and heavy rainfall associated with storm activity at the end of the month. Despite the devastating and tragic effects of both these events, they did not depress irradiance following the clear start to the month.
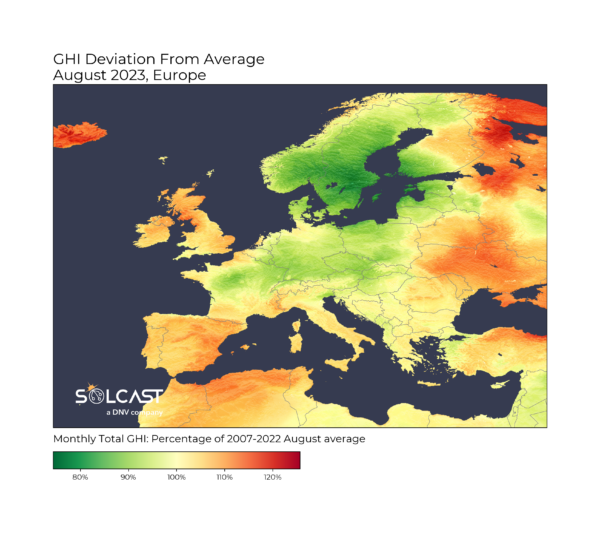
Most of Scandinavia recorded just 80% of average August irradiance, with central Europe seeing only 90% from France to Poland. In addition to the normal jetstream cloud effects, these regions were impacted early in the month by cloud cover associated with Storm Hans. This storm was the second unusually intense summer storm seen in the region, following Storm Poly in July, and it’s possible these storms are being intensified by the concentrated nature of the jetstream pattern this year. The impacts from this storm were significant, with the World Weather Attribution (WWA) declaring the rain in Germany a 400-year event, and railway infrastructure being impacted in a derailment in Denmark and a railway bridge collapse in Norway.
Popular content
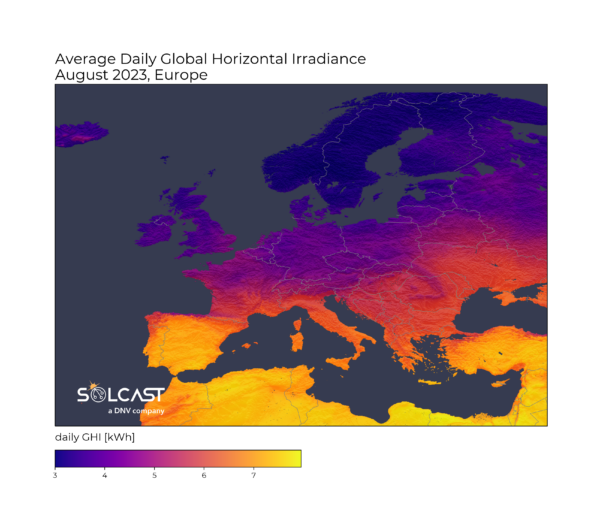
Spain typically leads August irradiance in Europe, so the effects of increased sunshine this year provide a stark contrast to the rest of the continent in the average irradiance map above. The Iberian Peninsula averaged more than 7 kWh/m2 across the month, despite the impacts of aerosols from the wildfires and the rain activity at the end of the month.
Solcast produces these figures by tracking clouds and aerosols at 1-2km resolution globally, using satellite data and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This data is used to drive irradiance models, enabling Solcast to calculate irradiance at high resolution, with typical bias of less than 2%, and also cloud-tracking forecasts. This data is used by more than 300 companies managing over 150 GW of solar assets globally.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.

1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.