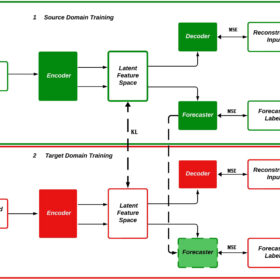
Domain adaptation framework for PV power forecasting
A team of researchers have developed a domain adaption framework capable of transferring knowledge from solar power plants with abundant data to plants that need to be trained without labelled data. The framework has been tested at three solar power sites in Germany and was found to perform better than reference models.
Photovoltaic trees can save forest cover
Research simulating a solar tree farm within a coastal forest in South Korea found that solar tree structures could preserve 99% of forest cover when compared to a fixed solar farm built in the same area, without sacrificing power output.
Novel MPPT methodology uses grey wolf hunting as inspiration
Researchers have developed a maximum power point tracking algorithm based on the social hierarchy and hunting strategy of grey wolves. When tested under realistic shading conditions, the grey wolf optimizer achieved an average MPPT efficiency of 98.15%, significantly outperforming conventional MPPT methods.
Self-powered electroluminescence for daylight PV system inspection
Scientists from Spain have developed a daylight electroluminescence method that uses other strings to supply current to the inspected string. It was simulated and then tested in two 50 MW PV plants. Comparative assessment against lab-electroluminescence resulted in acceptable diagnostic performance.
Weathered PV backsheets have 46% faster flame spread than unweathered counterparts
Researchers in Singapore have accelerated the weathering of PV backsheets and investigated their flame spread behavior at different intervals. After 6 weeks, they found that weathered PV backsheets show 46% faster flame spread than unwearthered ones. They have also highlighted that current safety standards fail to account for long-term degradation.
New deep learning tech for PV inverter fault diagnosis
A team of scientists in the United States has combined both spatial and temporal attention mechanisms to develop a new approach for PV inverter fault detection. Training the new method on a dataset created in MATLAB/Simulink, the group has compared it to a series of other data-driven and statistical-based methods and has found accuracy reached 97.35%.
Sungrow debuts 2.5 kW microinverter
The Chinese company said its new microinverter supports four independent MPPT inputs with DC input currents up to 18 A.
All-perovskite PV-powered battery for portable electronics
Scientists have used a dual-functional, material-sharing strategy with ethyl viologen diiodide to achieve synergistic performance enhancement in PV-powered batteries. The system was reportedly able to power a wearable glucose monitor for 24 hours.
Euronergy launches new lightweight PV module series
The Dutch company said the new products have a power output ranging from 410 W to 430 W in power and an efficiency of up to 22.2%. The panels reportedly weigh 30% less than conventional counterparts.
Using drones, satellite and ground data to map vegetation in PV plants
Scientists have developed a multi-scale method to assess vegetation conditions inside PV power plants. The research focused on nine PV plants in China across diverse climate zones. Compared to satellite estimates alone, the method reduces bias by 16.98%.