New soiling detection method based on drones, AI, image processing
Developed by scientists in China, the proposed approach uses mathematical morphologies for image processing, such as image enhancement, sharpening, filtering, and closing operations. It also uses image histogram equalization and edge detection, among other methods, to find the soiled spot.
Recursive least squares algorithms to detect abnormal operation in PV systems
Scientists in Spain have implemented recursive least squares (RLS) algorithms for anomaly detection in PV systems and have found they can provide “more realistic and meaningful assessment” than traditional energy analysis.
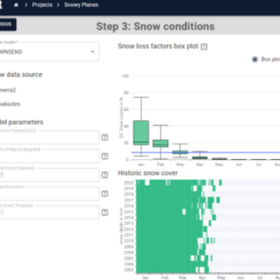
PVRadar offers solar project risk assessments factoring in historical climate data
PVRadar Labs has expanded its software platform to include PV project risk assessment functionality, reportedly enabling more realistic performance estimates based on historical climate data.
Novel hydrophobic, antireflective coating for solar glass
Slovakian scientists have developed a novel hydrophobic, antireflective coating for solar glass with a silica-titania thin film as the bottom layer and an inorganic-organic upper layer made of silica modified with triethoxy(octyl)silane. This new coating increases glass transmittance by 7% compared to uncoated glass.
Chemitek offers new cleaning products for floating PV
Chemitek has developed new cleaning products for floating PV arrays. The Portuguese company says it has tested and confirmed them to be safe for animals and vegetation around such systems.
Quantifying effect of cooling, cleaning in PV systems operating under desert conditions
Scientists in Oman have analyzed the effect of soiling, cleaning, and water injection on the performance of PV panels in Oman. They have found the use of water for cooling may increase power yield by up to 23.9%.
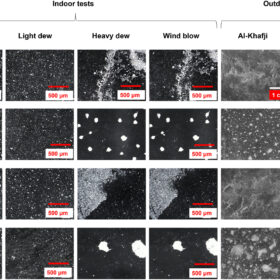
Scientists describe anti-soiling performance mechanisms in solar glass
Laboratory and outdoor soiling experiments conducted in Saudi Arabia have shown that increased particle resuspension by wind is one of the dominant factors for high anti-soiling performance in photovoltaic glass.
Deep-learning tech for dust detection in solar panels
Researchers from China and the UK have improved the Adam optimization algorithm to achieve better results in dust detection on PV panels. The optimized algorithm reportedly performed better than most common algorithms used for dust detection.
The effect of extreme dust conditions on PV system performance
Scientists in Romania have found that extreme dust conditions may cause losses of 45.35% and 38.14% in maximum power and short-circuit current under outdoor conditions for different kinds of solar modules. They warned that, if the effects of climate change escalate, resulting in less rainfall and more frequent sandstorm events originating from the Saharan region, extreme scenarios are very likely to occur in Europe.
New research shows impact of dust on PV module temperature, performance
New research from Pakistan shows that dust could reduce PV panel performance through the shielding effect and the “dust-temperature” phenomenon. The scientists tested two PV systems in different parts of the country.