Tin perovskite solar cell with operational stability of over 1,300h
Scientists in Spain have built a 10.61%-efficient tin perovskite solar cell with improved open-circuit voltage and stability. The device was fabricated with formamidinium tin iodide (FASnI<sub3), sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a reducing agent, and a bulky secondary ammonium cation of small size known as dipropylammonium iodide (DipI).
Endesa plans Europe’s largest hybrid wind-solar-storage plant
The hybrid facility is planned to be built in central Portugal. It will consist of a 365MW PV unit, a 264MW wind farm, and 168MW of battery storage. It will also be connected to a 500kW electrolyzer that will be fed with surplus power that cannot be stored by the batteries.
Spain’s PV capacity tops 15GW
According to new statistics from the Spanish grid operator, around 3.3GW of new PV systems were deployed in the country last year.
Latent heat thermophotovoltaic battery for renewables storage
Developed by researchers in Spain, the battery uses renewable electricity to melt low-cost metals such as silicon or ferrosilicon alloys to produce and store latent heat, which is in turn used by a thermophovoltaic generator to produce power. According to its creators, the device may store electricity at a cost of €10 per kilowatt-hour for a 10MWh system.
Mondragon, QHD Visual develop new laminator for solar module assembly
The new laminator is suitable for any type of photovoltaic module and is specially designed for glass-glass modules and new applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and vehicle-integrated solar.
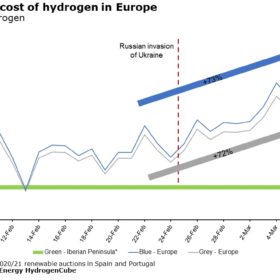
Invasion of Ukraine an inadvertent boost for green hydrogen
Rystad Energy has joined BloombergNEF with a significant forecast for gray and blue hydrogen off the back of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. According to the analysts, the impact of the war has sent prices of fossil fuel-tied forms of hydrogen production surging, leaving the gradual but consistent downward price trend of green hydrogen now looking remarkably competitive.
Storing renewable electricity with supercritical CO2 heat pump
Researchers in Spain have designed a pumped thermal energy storage system that uses supercritical carbon dioxide as a heat pump and a heat engine. The proposed system is claimed to achieve an efficiency of 80.26% and an LCOS of €0.116/kWh.
Investment cycle means race is on to incentivize green hydrogen
A report published by Irena hints the world’s politicians will have to get to work immediately to avoid another generation of fossil fuel-fired hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol plants being set up to run into the second half of the century.
Spanish consortium wants to produce green hydrogen with sewage
The Zeppelin project is expected to generate more than 135,000 tons of green hydrogen from 99 million tons of waste and 50 million tons of municipal wastewater.
Solarpack offers remote PV self-consumption to Spanish consumers
Solarpack’s click&go system relies on solar panels in its own projects, rather than in the homes of consumers, so households can consume renewable energy remotely. Clients can buy energy produced from their remotely owned panels for around €30 ($32.98)/MWh.