How can IEC standards help renewables adapt to climate change?
Renewable and clean energy is one of the most effective solutions to reduce carbon emissions, but they are also strongly affected by climate change. IEC Standards and conformity assessment can help them to be more resilient.
Lack of information, financing among barriers to UK’s heat pump adoption
A questionnaire and focus group study of households in the UK city of Bristol found residents have a lack of access to technical and ‘common sense’ information on the transition to heat pumps. Able-to-pay residents became more willing to invest as they learned about the technology.
Uncovering attitudes towards agrivoltaics via community engagement
An American research group has conducted a pilot workshop for agrivoltaics stakeholders in Arizona, including farmers, developers, government officials and indigenous leaders. A reflection paper offers some key takeaways for future public participation.
PV industry could account for 40% of global silver demand by 2030
New research from Europe shows that the global PV industry may require up to 14,000 tonnes of silver per year in 2030, with global supply being only 34,000 tonnes. The scientists said more efforts should be made to reduce silver content in TOPCon and heterojunction solar cells.
Powering ferries with floating PV, hydrogen
Scientists in Malaysia have conducted a techno-economic-environmental study of a green fueling system for a ferry that runs between islands in their home country. Using 40,000 solar panels, they were able to power two round trips round-trips per day. Annual CO₂ reduction was measured at 23.75 million kg.
Decision making tool for crop selection in agrivoltaics
Researches in Germany have created a comprehensive crop selection tool for agrivoltaics across more than 25 countries. The proposed matrix evaluates species-specific responses of 12 major crop types to shading, microclimate changes, and crop growth, while also assessing their water needs, shade tolerance, and space requirements.
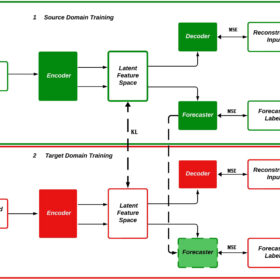
Domain adaptation framework for PV power forecasting
A team of researchers have developed a domain adaption framework capable of transferring knowledge from solar power plants with abundant data to plants that need to be trained without labelled data. The framework has been tested at three solar power sites in Germany and was found to perform better than reference models.
Photovoltaic trees can save forest cover
Research simulating a solar tree farm within a coastal forest in South Korea found that solar tree structures could preserve 99% of forest cover when compared to a fixed solar farm built in the same area, without sacrificing power output.
Saharan dust events can reduce PV power output in Mediterranean area by up to 50%
New research from Hungary shows that Sarahan dust events can reduce PV power output in five Mediterranean countries by an average of 25-40%. The scientists stressed the need for including real-time dust monitoring and cloud interactions in solar forecasting.
Novel MPPT methodology uses grey wolf hunting as inspiration
Researchers have developed a maximum power point tracking algorithm based on the social hierarchy and hunting strategy of grey wolves. When tested under realistic shading conditions, the grey wolf optimizer achieved an average MPPT efficiency of 98.15%, significantly outperforming conventional MPPT methods.