Assessing the impact of micro-cracks in solar glass
A Turkish research team has analyzed how big changes in temperature can affect absorbance, light transmittance and reflectivity in two types of solar glass. The scientists demonstrated lower efficiency in solar cells and the glass itself were attributable to a large number of micro-cracks and deformations on the glass surface.
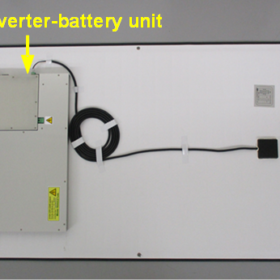
Downsizing silicon carbide inverters
Japanese researchers have investigated the effectiveness of SiC devices in sub-kilowatt applications. A 790g device was tested in a mini PV generator system which included a battery and maximum power point tracker circuit in the same housing. Compared to traditional mini inverters the SiC device showed 3% higher efficiency.
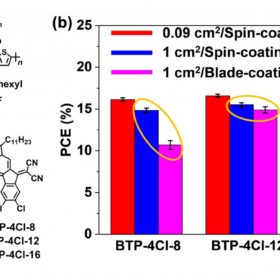
New non-fullerene electron acceptor for 17% efficient organic solar cell
Chinese scientists have developed a cell with a new blade-coating method and BTP-4Cl-12, a kind of acceptor that is a derivative of the Y6 acceptor, which is widely used in organic PV applications. The researchers also claim that the cells can maintain good efficiency levels, even if its surface is lightly expanded.
A titanium solar cell with 24% efficiency
The Australian research team which developed the device said the higher efficiency was achieved through a nanowire design which eliminates the interface inside the titanium dioxide band.
An inverted perovskite cell with 22.3% efficiency
Saudi researchers have developed a cell which is said to exhibit improved structural and optoelectronic properties as well as enhanced carrier mobility and diffusion lengths. The feat was achieved by reducing voltage losses using a new passivation technique.
Trimming optical losses in tandem perovskite cells
Spanish researchers have unveiled a monolithic nano-structured perovskite silicon tandem device they claim can reduce optical losses by more than a third compared to planar perovskite cells of the same kind.
Russian scientists unveil new manufacturing process for III-V solar cells
Researchers have integrated A3B5 semiconductors on a silicon substrate in a prototype solar cell and claim the technique could enable the production of III-V solar cells with conversion efficiencies of around 40%.
Greening greenhouses with organic PV
Semi-transparent organic solar cells can reduce the carbon footprint and raise the crop yield of greenhouses while acting as generators and insulation. Scientists in the U.S. say greenhouses equipped with organic cells could be energy self-sufficient year round in hot and moderate-humidity climates.
Improving magnesium-based batteries with chaos
Researchers have found strong anodic activity in disordered particles of magnesium chromium oxide. Unlike conventional, ordered nanocrystals, the disordered particles reportedly achieved reversible magnesium extraction and insertion.
Silicon heterojunction solar cell hits 23.5% efficiency with new hole-selective contact
Researchers from Switzerland’s École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne have used molybdenum oxide as the hole-selective contact in an heterojuction silicon cell. The scientists claim the compound can compete with traditional contacts despite a lower level of optimization.