Multiple effects of potential-induced degradation on solar module performance
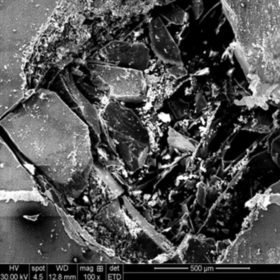
UK researchers have analyzed the multiple effects of PID on 28 modules at an outdoor testing field. The novel approach considered all multiple PID effects through a comprehensive analysis, which included power losses, hotspots, mm-level defects, and the performance ratio.
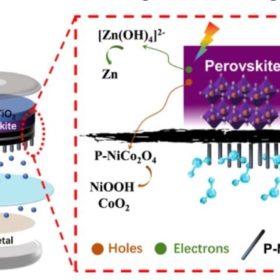
PV-powered rechargeable aqueous zinc battery
Conceived by scientists in China, the device combines an integrated carbon-based perovskite solar cell module with a rechargeable aqueous zinc metal cell. The proposed system achieved an overall efficiency of 6.4%, and a steady operation for more than 200 cycles with little performance degradation.
India targets domestic production with 40% PV import duty, boost to manufacturing-linked incentive
India’s Union Budget, presented this week by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, allocates an extra INR 19,500 crore ($2.6 billion) to the production-linked incentive scheme for solar from April.
Perovskite solar cell with 24.18% efficiency via low-dimensional perovskitoids
Chinese scientists used perovskitoids as 1D and 0D capping layer materials for the cell’s perovskite layer. These materials enabled an effective and all-around passivation of the perovskite surfaces and grain boundaries, which prevents undesired Shockley-Read-Hall recombination and material degradation. The device achieved a power conversion efficiency of 24.18%, an open-circuit voltage of 1.151 V, a short-circuit current of 25.96 mA/cm2, and fill factor of 80.91%.
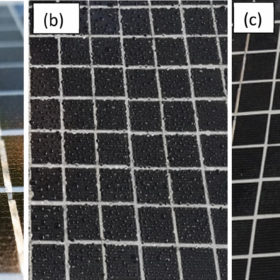
Titanium wires-based anti-soiling coating to improve solar module yield
Researchers in Thailand have developed an anti-reflective and anti-soiling coating for commercial solar modules that is claimed to increase power yield by over 6%. The coating has photocatalytic properties that make the organic compounds adsorbed on the solar module surface decompose, thus preparing them to be easily washed off by rainwater.
Sun-tracking tessellated photovoltaic array for use in space-restricted areas
Created by scientists in Korea, the shape-transformable 3D PV system is claimed to be able to increase electricity yield by 60% over a day compared to a fixed flat panel due to the shorter shadow length and the bifacial effect obtained during shape transformation. The proposed system doesn’t need any machinery to follow the sun and its developers said it would be a perfect solution for both urban and rural environments with limited space.
Perovskite solar cell with record-breaking fill factor of 86.6%
An international group of researchers has achieved the highest fill factor reported for perovskite cells of any size to date. The device was fabricated with a nitrogen-doped titanium oxide (TiOxNy) electron transport layer aimed at improving charge transport between the cell’s perovskite absorber and the electrodes.
Multi-level fin heat sinks for solar module cooling
Developed by Malaysian scientists, the proposed multi-level aluminum fin heat sinks (MLFHS) were found able to reduce the module operating temperature by up to 8.45 degrees Celsius and increase power yield by up to 10.75%. The system cost was estimated at $0.60/W.
The panel and the city
US researchers have investigated how rooftop PV systems may affect air and building temperature in urban environments and, conversely, how the urban heat island (UHI) effect may have a negative impact on PV system performance. Their work considered urban air temperature, urban air pollution, the partial shading of the PV system, soiling, building heating and cooling loads, and outdoor shade.
Perovskite solar module with 18.45% efficiency via co-solvent dilution strategy
The module was fabricated with methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) perovskite solar cells via low-cost spin coating. The panel also achieved an open-circuit voltage of 16.07 V, a short-circuit current of 69.52 mA, and a fill factor of 75.35%.