From pv magazine USA
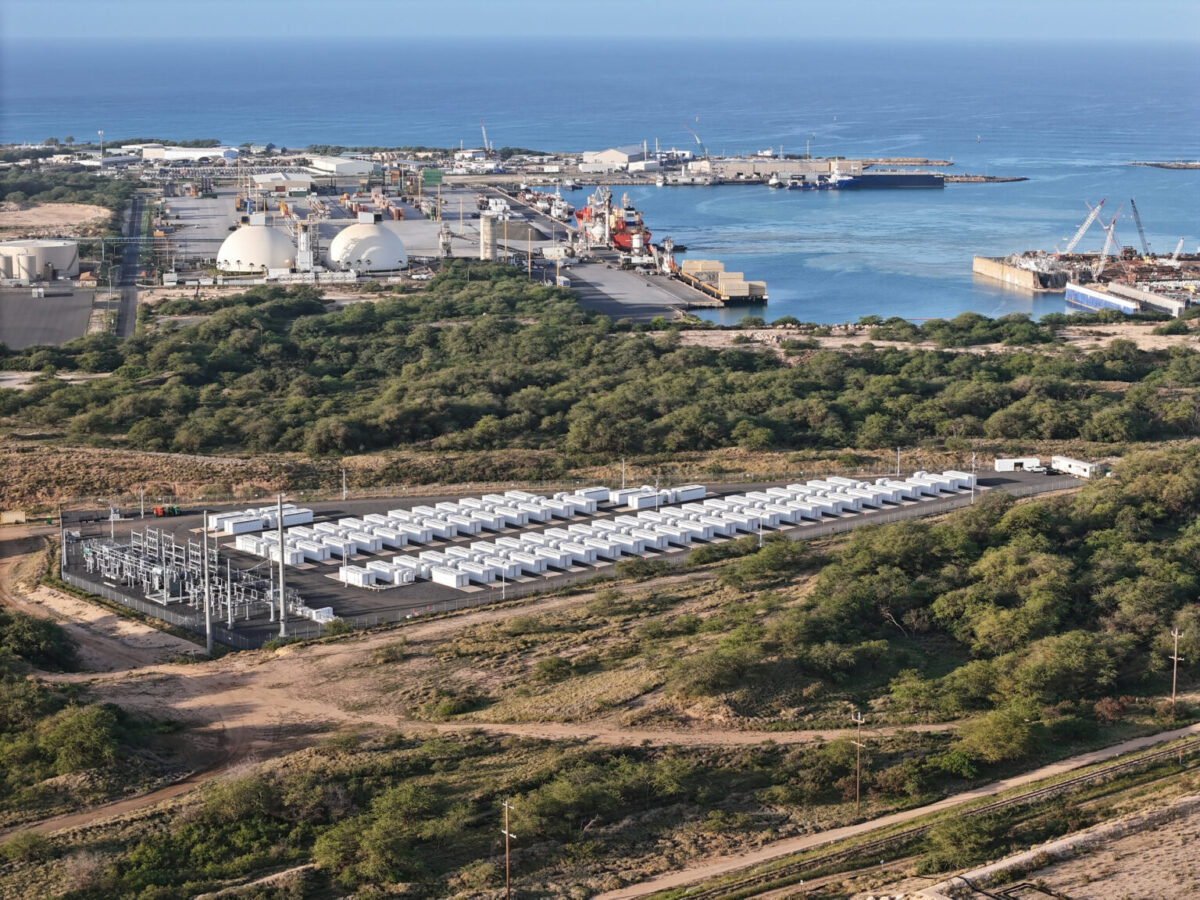
Plus Power has started operating its Kapolei Energy Storage (KES) facility on Oahu, Hawaii, helping the state in its transition from fossil fuels to solar and wind.
The KES project adds 135 MW/540 MWh to the Hawaiian Electric grid, with an additional 50 MW/25 MWh of additional “fast frequency response” to support grid stability.
The advanced battery has “virtual inertia” to replicate the power-smoothing function of a conventional spinning turbine. It has “black start” capabilities, which supports grid recovery in the event of a blackout.
“It’s the first time a battery has been used by a major utility to balance the grid: providing fast frequency response, synthetic inertia, and black start,” said Brandon Keefe, executive chairman, Plus Power. This project is a postcard from the future – batteries will soon be providing these services, at scale, on the mainland.”
Located on 8 acres of industrial land on the southwest side of Oahu, the project is comprised of 158 Tesla Megapack 2 XL lithium-ferro-phosphate batteries, each about the size of a shipping container.
The battery can serve as a grid “shock absorber,” serving a role normally performed by combustion-powered plants. It can respond to grid signals in 250 milliseconds, far faster than the several minutes that conventional power plants take to fire up.
“Energy storage technology that responds quickly to constantly changing conditions is an essential tool for us to use to manage the grid and operate it as efficiently as possible,” said Jim Alberts, senior vice president and chief operations officer, Hawaiian Electric.
Solar power has become abundant, leading Hawaiian Electric to have to curtail, or turn off, large volumes of utility-scale solar and wind to keep the system in balance. The new energy storage capacity is expected to allow the utility to reduce renewable energy curtailments by 69%. It is also expected to enable 10% more new utility-scale renewables on the grid than previous models allowed.
Hawaiian Electric said it expects the battery to save its customers on electricity bills. The utility estimates the battery will reduce electric bills by $0.28 per month over its 20-year contract life.
The KES battery plant is interconnected near three of Hawaiian Electric’s critical power generation facilities, enabling a rapid reboot of those power plants in the event of an island-wide emergency. This is known as “black start” capability.
The batteries will help replace grid capacity formerly provided by an AES coal-fired power plant less than a mile away. The plant used to provide about 20% of Oahu’s electricity, home to nearly one million residents. The plant closed in September 2022.
Project developer, owner, and operator Plus Power has a development portfolio of over 10 GW of projects in transmission queues across 28 states and Canada. It has over $1.8 billion in project financings announced as of October 2023. The company expects to be operating seven additional large-scale energy storage plants across Arizona and Texas, adding 1325 MW / 3500 MWh of storage by June 2024.
“Our projects, like KES, help our customers provide affordable, reliable, clean electricity on hot summer afternoons and cold winter nights, while enabling the decarbonization of the electric grid,” said Keefe.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.



2 comments
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.