From pv magazine Germany
The sharp price drop for solar modules in November might mark the end of the ongoing decline, as the market shows signs of recovery.
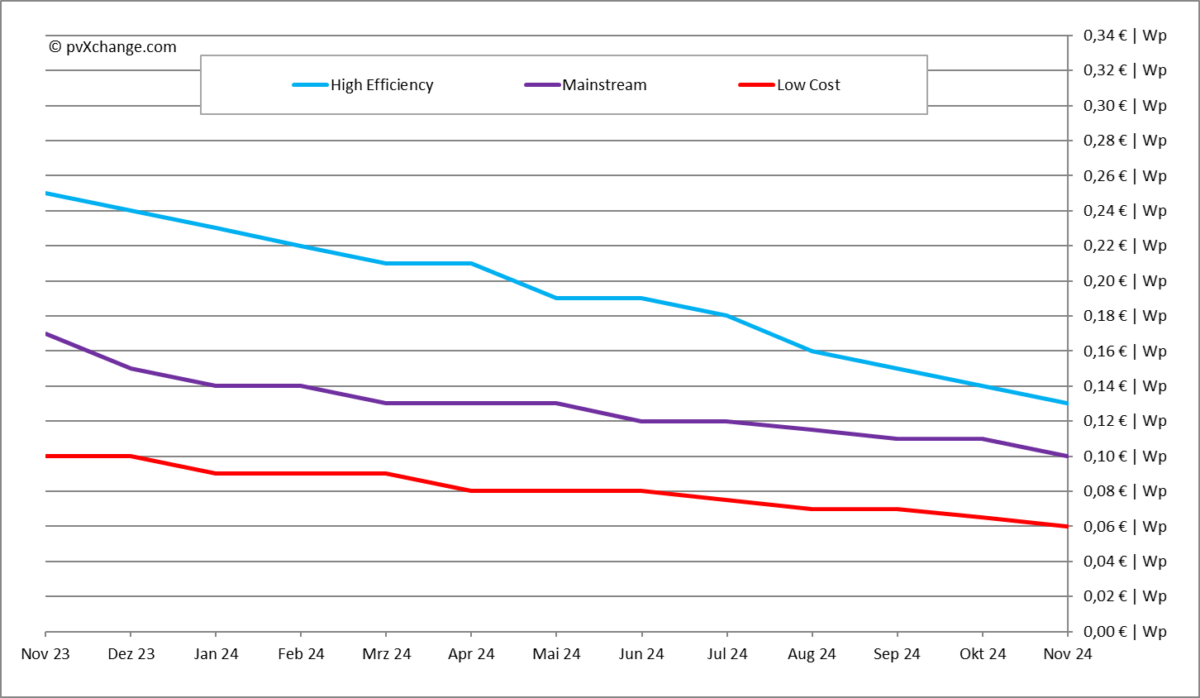
Prices fell by an average of 8% across all technologies, squeezing margins even on recently purchased modules. This drop resulted from moderate demand, year-end stock clearance campaigns, and insolvency-related emergency sales.
Some modules are now selling for under $0.06/W, but experts warn against low-quality, no-name products, citing operational risks and unreliable guarantees from second- or third-tier Chinese manufacturers.
The downward trend appears to be reversing. China's export tax rebate on solar modules, long set at 13%, dropped to 9% on Dec. 1, raising exporters’ costs by 4%. This change could increase module prices by $0.03/W to $0.05/W.
More significantly, manufacturers are reducing production to engineer an artificial supply shortage. Capacity cuts in China, reduced exports, and factory shutdowns over the winter aim to restore profitability. This strategy, if effective, could transform the market into a seller’s market where suppliers dictate prices.
How quickly this strategy succeeds depends on the volume of existing stock in Europe. Adequate supply could limit the impact of production cuts, particularly for mainstream modules. Premium products, such as bifacial glass-glass modules with high efficiency, may see sharper price increases, widening the gap between mainstream and high-efficiency offerings. Budget modules may still be available at bargain prices.
Market players are acting cautiously, with some reversing cancellations for surplus goods and securing inventory. Projects with solid pipelines are hedging against future shortages by purchasing now. If an end-of-year rush depletes stocks, it could trigger the price increases suppliers anticipate – even modest stimuli like minor tax changes could drive such a shift.

About the author: Martin Schachinger has studied electrical engineering and has been active in the field of photovoltaics and renewable energy for almost 30 years. In 2004, he set up the pvXchange.com online trading platform. The company stocks standard components for new installations and solar modules and inverters that are no longer being produced.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.