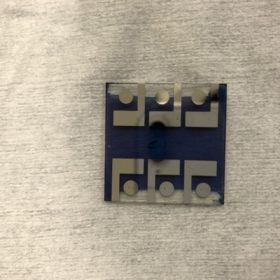
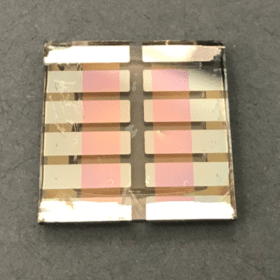
Semitransparent dye-sensitized solar module for BIPV applications
Scientists in Italy have developed a module with an area of 0.2 sm and an efficiency of 2.7% in outdoor conditions, with a tilt angle of 60 C. They designed it by considering the trade-off between low losses and device sturdiness.
Green solvents for a 17%-efficient organic solar cell
Scientists in Sweden and China developed a solution-based process to produce organic solar cells, demonstrating efficiencies better than 17%. The process utilizes paraxylene as a solvent, which the researchers claim is less toxic and more stable than others used to reach high organic solar cell efficiencies, and with more work could be scaled up to produce large area devices.
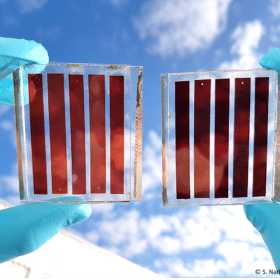
Semi-transparent solar module for greenhouse applications
Manufactured by scientists in Italy, the 3.88%-efficient organic solar panels are able to filter the light from the roofs of greenhouses. They are also capable of supplying a portion of the electricity required to power the greenhouse’s temperature and humidity sensors.
Nanocomposite films for 13.57%-efficient organic solar cell
Scientists in Malaysia have used, for the first time, nanocomposite films based on zinc oxide and polyvinyl alcohol in organic solar cells. These films were able to improve the efficiencies of the PV devices by up to 3.5%.
Organic solar cell with 18.4% efficiency via new electrode coating
Saudi scientists built the cell’s electrode with a hole-transporting molecule called Br-2PACz and not with the commonly used PEDOT:PSS. It helped improve the photovoltaic cell efficiency by around 0.9%.
Organic solar for optical wireless data receivers
Researchers in the United Kingdom have built a 14%-efficient organic PV device that can be used in high-speed optical wireless communication systems. The cell consists of a 4×2.5mm photoactive layer fabricated with a bulk heterojunction of a polymer donor and fullerene and non-fullerene acceptors.
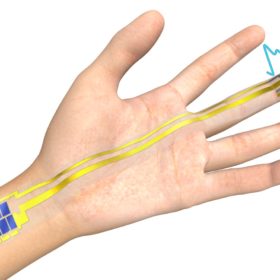
I’ve got solar over my skin
Researchers in Japan have built a PV-powered device to measure volumetric variations in blood circulation. The system, which is just a few microns thick, was built with an organic solar module, a polymer light-emitting diode (PLED), and an organic photodetector.
Semi-transparent dye-sensitized solar module with 8.7% efficiency
The mini-panel showed a short circuit current of 58.1 mA, an open circuit voltage of 3.63 V, and a fill factor of 58.26%. It has a power output is 122.9 mW and an active area of 14 cm2.
Even if it is cheap enough, efficiency does matter
A British-German research team claims that organic PV technologies may become mature enough to compete with crystalline silicon and thin-film products not only in BIPV, but also in power generation in the electricity market. In order to get there, however, organic PV products will have to achieve higher efficiencies.
AI model for accurate prediction of organic PV efficiency
Over the last few months, Nastaran Meftahi has been spending her time in pandemic lockdown developing a machine-learning model to predict the future of next-generation organic solar cells.