Alfanar to build 110 MW of solar for desalination plant in Saudi Arabia
Alfanar has revealed plans to set up a solar project including ground-mounted and floating PV to provide power to the Al Jubail 2 water desalination plant on the east coast of Saudi Arabia. It will require an investment of SAR 1.2 billion ($319 million).
The Hydrogen Stream: Penta-Ocean opens factory exclusively powered by solar, hydrogen
Japan’s Penta-Ocean has opened a new factory powered by a 670 kW PV system and fuel cells. Plug Power, meanwhile, has revealed that it will provide fuel cells, hydrogen storage, and fueling infrastructure to FreezPak Logistics.
Turkey provides $410 million for 2 GW solar module factory
Smart Solar Technology has secured Turkish government support to build a vertically integrated solar module factory in Izmir, Turkey.
Poland to allocate 9 GW of solar in 2022-27 auctions
The Polish government plans to allocate around 13 GW of new renewables capacity under a six-year scheme. It said 4.5 GW of solar will be assigned to projects above 1 MW in size, while another 4.5 GW of capacity will be assigned to smaller installations.
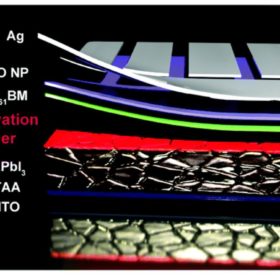
Inverted perovskite solar cell hits 21.4% efficiency with Ruddlesden-Popper passivation layer
South Korean scientists have used a vertically oriented passivation layer, featuring two-dimensional Ruddlesden-Popper perovskites (RPP), to mitigate nonradiative recombination in inverted perovskite solar cells. They achieved the highest efficiency ever reported for a perovskite cell formed by vacuum deposition.
Underground heat exchanger to cool down solar panels
Spanish scientists have built a cooling system featuring heat exchangers on solar panels and U-shape heat exchangers installed in a borehole at a depth of 15 meters. The researchers claim that this reduces panel temperatures by up to 17%, while improving performance by about 11%.
Recom launches bifacial heterojunction solar panel with 395 W output
Recom’s newest solar panels feature efficiencies of up to 21.68% and a temperature coefficient of -0.24% per degree Celsius. The company is offering a 30-year power output guarantee for 91.25% of the initial yield.
Australian manufacturer unveils solar tile with 19.3% efficiency
Leeson Group, a Melbourne-based renewable energy company, has developed a rooftop PV tile with an efficiency rating of up to 19.3%.
Portugal offers remuneration boost to solar auction winners
The Portuguese government said in a new legal decree that it will adjust the prices, according to inflation, of winning bids from its record-breaking solar auctions in 2019 and 2020. It will also extend the period during which projects can sell electricity at spot market prices by 12 months.
Mondragon Assembly to develop multi-gigawatt automated manufacturing line for BVG
It will be one of the largest and most automated lines in North India, with the capacity to produce high power modules with larger cells. The first phase will have a production capacity of 500 MW.