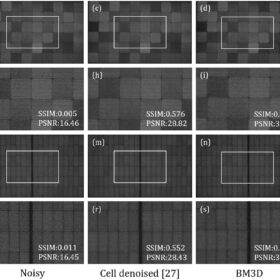
Denoising outdoor electroluminescence images of PV panels through deep learning
Researchers in Australia have developed a simplified residual network-based architecture method to filter out noise from electroluminescence images of PV modules. The proposed technique reportedly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of automated inspection systems for utility-scale PV plants.
Water-based photovoltaics reach global capacity of 21.18 GW
An international research team has developed an index-based remote sensing method to see trends in the global development of water-based PV. It has found that China currently accounts for 80% of the global total deployed capacity.
CSP-driven multigeneration system combines hydrogen generation with compressed air, pumped hydro storage
Researchers have designed a novel multigeneration energy system that provides five outputs, namely electricity, hydrogen, cooling, heating, and hot water. The system is mainly powered by a solar heliostat system and incorporates compressed air and pumped hydro storage technologies for storing surplus power.
Testing 54 different combinations of solar-assisted heat pumps
Researchers in Germany have modeled dozens of indirect-expansion solar-assisted heat pump systems using photovoltaic-thermal panels for single-family homes in Munich, Berlin, and Hamburg. Simulations accounted for local weather, electricity use, and thermal demand.
Hoarfrost-inspired technique to improve MPPT in PV systems under partial shading
Scientists in China have introduced developments to the RIME optimization method, which takes inspiration from the developmental course of hoarfrost in nature. They have compared it to other MPPT algorithms and found it to be faster and to improve power output.
Birds thriving, breeding successfully in Germany’s solar parks
Larks and other bird species are flourishing in Germany’s solar parks, where breeding success exceeds that of many other habitats. These PV project sites are becoming valuable refuges, benefiting both wildlife and the surrounding environment.
Ivory Coast launches tenders for 200 MW/66 MWh of solar-plus-storage
Ivory Coast has opened tenders for 200 MW/66 MWh of solar-plus-storage, seeking proposals for two 100 MW solar parks each connected to 33 MWh of storage.
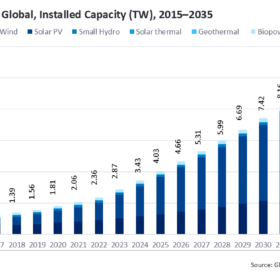
Global solar capacity to surpass 7.5 TW in 2035, says GlobalData
UK consultancy GlobalData projected, in figures shared with pv magazine, that global renewable capacity could hit 11.2 TW by 2035, led by solar. It expects cumulative PV capacity to hit 2,378 GW by year-end and 2,849 GW by 2026.
Deploying floating PV on mine pit lakes, tailings ponds
Researchers in South Korea have conducted a literature review on recorded cases of floating PV plants placed on mine pit lakes and tailings ponds, both of which are byproducts of the mining industry. Looking at more than dozens of cases, they have concluded that mine pit lakes generally provide more stable environments for deployment.
Hybrid deep learning model for PV forecasting in scenarios with considerable fluctuations
Researchers in China conceived a new PV forecasting approach that integrates causal convolution, recurrent structures, attention mechanisms, and the Kolmogorov–Arnold Network (KAN). Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms 10 existing forecasting models.