Longi builds 27.25%-efficient back-contact solar cells with high-resistivity wafers
High-resistivity silicon wafers offer superior efficiency potential but are highly sensitive to edge recombination and mechanical damage, limiting their commercial use compared to more robust standard wafers. Researchers from Longi and Sun Yat-sen University demonstrated that integrating in-situ edge passivation unlocks this potential, significantly boosting back-contact solar cell fill factor and efficiency.
Polysilicon transactions remain subdued amid buyer hesitancy
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
SALD launches large area sheet-to-sheet tool for perovskite solar pilot lines
The Dutch spatial atomic layer deposition equipment manufacturer has launched a new sheet-to-sheet tool for pilot production of large area perovskite solar devices on glass substrates.
UV testing, solar cell factory inspection now mandatory for Munich Re’s PV warranty insurance
The world’s largest reinsurer has recently introduced stricter requirements for PV warranty insurance to further de-risk insured PV parks and set a higher benchmark for industry wide reliability and production quality.
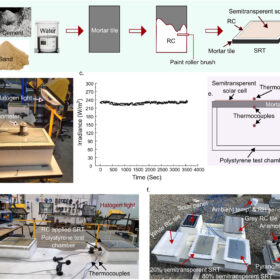
New reflective coating increases BIPV power output by 11%
Australian researchers developed a low-cost reflective coating for semi-transparent solar roof tiles that lowers surface temperatures by up to 20 C and boosts power output by up to 11.7%. Simulations across five global cities showed energy savings of up to 5.85%, highlighting the coating’s strong potential for improving both building cooling efficiency and solar performance in BIPV systems.
Retrofit coloring solution makes conventional solar panels less visible
Fraunhofer CSP researchers in Germany are developing printing and color technologies to make conventional silicon PV panels less visible when installed on building façades, roofs, and balconies.
South Korea’s Won Kwang S&T launches mobile solar panel recycling solution
Won Kwang S&T has developed a mobile, on-site solar module recycling system for utility-scale PV plants. The SolreBorn unit can reportedly process up to 2.5 tonnes of modules per day and improve the economics of solar panel recycling through on-site dismantling and material recovery.
China expects up to 287 GW of new PV capacity additions in 2026
China’s PV industry expects 238 GW to 287 GW of domestic capacity additions in 2026 as it pivots away from volume-led growth after a loss-making year driven by overcapacity and sharp price declines. The shift follows rapid expansion in 2021-25 that lifted cumulative capacity above 1.2 TW, annual additions beyond 300 GW and exports over $180 billion.
DAS Solar unveils new method to identify hot-spots in TOPCon back-contact solar modules
The Chinese manufacturer said it developed a new circuit-model–based method to accurately detect hot-spot risks in TOPCon back-contact modules, overcoming limitations of the IEC 61215 approach caused by low shunt resistance. Validated through indoor and outdoor tests, the method predicts temperature rise under shading and reportedly enables faster, more accurate hot-spot risk assessment.
United Solar begins production at Omani polysilicon factory
The factory is located in Oman’s Sohar Freezone and will be capable of supporting the production of up to 40 GW of solar modules annually once at full capacity.