India’s Borosil to expand solar glass production capacity to 2,000 tons per day
The solar panel glass manufacturer expects strong growth in demand for its products at home and abroad with a significant rise expected in the production of PV modules in the USA and Europe.
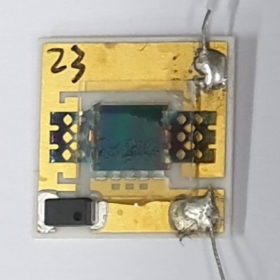
Multi-junction solar cell integrating radiative cooler
The triple-junction solar cell is based on indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and Germanium (Ge) and is made with a micro-grating made of glass, consisting of a two-dimensional x-framework structure fixed onto the surface of the solar cell. Its operating temperature was found to be 6 degrees Celsius lower than that of a reference cell without the cooling technique.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: GCL-Poly wants to move to Shanghai Stock Exchange
In other news, Longi raised funds to build another 18 GW of solar cell capacity and Suntech began work on its 10 GW module factory in Anhui Province.
Portable, space-saving photovoltaic towers
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi have developed solar towers that can be moved from one place to another and can generate 20-30% more power while requiring only 50-60% space compared to conventional mounting setups.
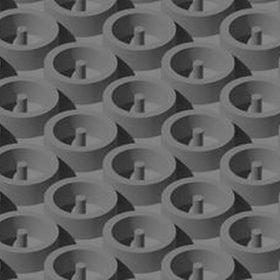
Subwavelength antireflective structure for thin-film solar cells
Consisting of a two-dimensional (2D) array of rings and pillars, the structure can improve the short-circuit current of a thin-film crystalline solar cell by over 50%, its creators say. The subwavelength AR structures are robust to certain degrees of fabrication errors, they add.
Average silver price expected to drop 1% to $24.80 per ounce this year
According to the Silver Institute, global industrial silver demand is expected to grow 8% this year due to strong demand in all key sectors, including the PV industry.
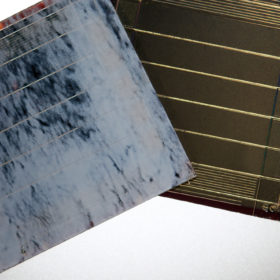
Small-area, colored perovskite BIPV module with 13.9% efficiency
Through a conventional coloring technique for crystalline solar modules, scientists in Germany were able to manufacture a colorized small perovskite solar module in white marble optic displays that maintains up to 88.5% of the efficiency it had before coloring. The device was built with five cells interconnected in series and has a total area of 9cm2.
Making the case for perovskite quantum dots
Quantum dots, a type of semiconductor based on tiny nanometer sized particles, are a cause for excitement in many disciplines thanks to their unique electronic properties. In solar cell technology, quantum dots fabricated from perovskites could have several advantages over more commonly researched “bulk” perovskite materials, and researchers are beginning to take note of these. A group of scientists in China evaluated recent progress in perovskite quantum dot solar cells, noting both strong potential and a long way to go for this early-stage technology.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: JA Solar increases production capacity in Vietnam, IDG Energy enters solar business
JA Solar is expected to put another 3.5GW of cell capacity into operation by the end of June and Hong Kong-based IDG Energy Investment will venture into cell manufacturing by establishing a “foreign invested” project company.
Powering up PERC-perovskite tandem cells
Perovskite-silicon tandem cells offer one of the surest pathways to much higher solar efficiencies, one that has moved close to commercialization in the past few years. Much of the work getting to this stage has naturally focused on developing a viable perovskite top cell. Optimizations to the silicon layer underneath, however, will also be important to the overall device function and efficiency. Scientists in Germany examined five different silicon cell concepts similar to those in mass production today, finding that with a few optimizations these could reach efficiencies up to 30.4%.