Features driving efficiency complicate solar cell disassembly, recycling
Researchers in Germany have sought to identify the features that may define the “ideal recyclable solar cell” and have found that the recyclability of PV devices is usually in contrast with the efforts of reaching high efficiencies.
Recycled silicon powder from end-of-life solar panels can be reused in anti-corrosion coating
Researchers in India have demonstrated a wet chemical process to recover silicon with high purity from end-of-life solar panels, which they used to make functionalized silica nanoparticles. Tests of the processed nanoparticles in anti-corrosion coatings showed a corrosion protection efficiency of 99.5 %, which they said was 200 times lower corrosion rate compared to uncoated silica nanoparticles.
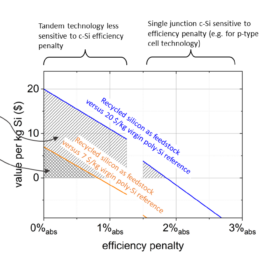
Prospects for reusing silicon from end-of-life solar modules in new ingot production
Scientists in the Netherlands proposed a new testing scheme for recycling silicon from end-of-life photovoltaic panels. Their methodology helped create different wafer categories for recycling silicon for new ingot production but also showed that most of recycled silicon in the near future will come from p-type products, which will harldy be reutilized in a market now dominated by n-type modules.
New tech to recover high-purity silicon powder from end-of-life solar panels
Korean researchers have used thermal and wet gravity separation (WGS) to separate EVA from reclaimed silicon powder in end-of-life PV modules with “minimal” chemical usage. The proposed technique provides silicon powder that could be reused as a raw material for upcycling into silicon nitride, silicon oxide, or silicon carbide.
Using deep eutectic solvents to separate EVA films from end-of-life PV modules
A Chinese-Australian research team has used for the first time deep eutectic solvents for separating EVA films for end-of-life PV panels. The result is reportedly a 100% separation rate accompanied by an aluminum removal efficiency of 98.4%
Australian solar panel recycler partners with Canadian silicon anode developer
Australia-based solar panel recycling company Lotus Energy has signed an agreement with Canadian silicon anode developer Neo Battery Materials with aims to supply future North American electric vehicle and energy storage needs.
Critical mineral report highlights Australia’s solar panel recycling potential
A new report published by the CSIRO says Australia’s research into solar recycling is second in the world, outside China, but suggests the establishment of mid-stream activities such as the production of metallurgical silicon and polysilicon have big potential.
AGL partners with Elecsome on solar panel recycling plan
AGL Energy has teamed with solar panel recycler Elecsome to explore the development of a PV materials recovery facility at the site of the coal-fired Bayswater power plant in New South Wales, Australia.
Three-step process to recover lead from end-of-life solar panels
Researchers in India have developed a new solar module recycling process that transforms lead into less toxic lead monoxide. It consists of three main steps – leaching, precipitation, and calcination.
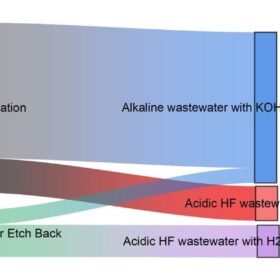
New water circulation tech promises lower PERC solar cell manufacturing costs
A German team developed models to illustrate water-saving potential in PERC silicon solar cell manufacturing based on a circular approach and commercially available technology. In the case of a 5 GW fab, water savings of up to 79% and wastewater discharge reductions up to 84% could be achieved, a “significant” improvement compared to a reference scenario.