Understanding why cesium and rubidium salt improve the yield of perovskite solar cells
The addition of either salt enables more even distribution of halide atoms within the perovskite material – key to increasing cell conversion efficiency. The explanation should speed up the process of identifying the best perovskite mixes.
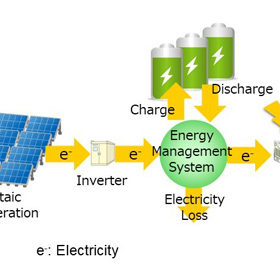
Japanese scientists seek to lower costs of PV-powered hydrogen
A research team has conducted a demonstration of the economic feasibility of battery-assisted, low-cost hydrogen production from solar. The scientists claim their system will mean hydrogen could be produced for $0.15-0.25 per cubic meter in 2030.
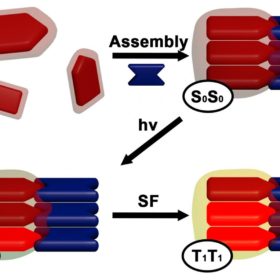
Singlet fission may raise theoretical efficiency of solar cells to 44%
According to a U.S. research team, new nanomaterials relying on dyes based on diketopyrrolopyrrole and rylene can generate a singlet fission reaction that extends the life of harvestable electronic charges.
Scatec Solar’s 65 MW Malaysian plant reaches commercial operation
It is the first of three solar parks of that size the Norwegian IPP has put in commercial operation in Malaysia’s growing market.
Clustering-based computation used to measure PV module degradation
The method could be an effective tool to measure the performance of solar modules, according to research, due to its ability to speed up the inspection process, preventing further damage and hastening repairs.
Iron therapy for solar cells
A research team from Sweden has developed a new iron-based molecule, which it says has the potential for further cost reductions in solar cells, and can also function as a photocatalyst to produce fuel.
Fluorinated electron-acceptor improves yield of organic thin film solar cells
A Japanese research team claims to have tailored an electron-accepting unit, which has been successfully used in an organic semiconductor applied in a solar cell device that showed high PV performance.
“Optical Tweezers can benefit solar cell research” – Interview
pv magazine interviewed Ricardo Arias González, who holds a PhD in Physical Sciences and introduced the Optical Tweezers applied to biology in Spain. It is one of the tools of photonics for which Arthur Ashkin received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2018, together with Donna Strickland and Gérard Mourou.
US scientists create MPP algorithm to measure PV panel degradation
The algorithm is said to be able to examine the relationship between weather forecast data and the projection of electric circuit parameters. Through this innovation, Purdue University researchers claim they can interpret the routinely collected maximum power point (MPP) time-series data, to assess the time-dependent “health” of installed solar modules.
Researchers propose doubling today’s solar panel efficiency using two weird tricks
By double stacking a perovskite-silicon solar cell and using the cell in a glass-on-glass bifacial solar module, scientists model that a 30-36% efficient solar module can be attained.