A team of scientists from the U.S. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and Sandia National Laboratories has proposed to use aluminum hydride (AlH3) to store hydrogen. This solid-state metal hydride, which is also known as “alane,” is commonly used for rocket fuel, explosives, as a reducing agent in alkali batteries, and as a hydrogen source for low-temperature fuel cells.
According to the researchers, this material is able to overcome the challenge represented by the thermodynamic limitation of hydrides in storing hydrogen. “Many high-capacity metal hydrides suffer from poor thermodynamics of hydrogen uptake after initial release, which necessitates extreme hydrogen pressures to regenerate,” the scientists explained. “Such a limitation is often tied to their metastable nature and hinders their real-world applications.”
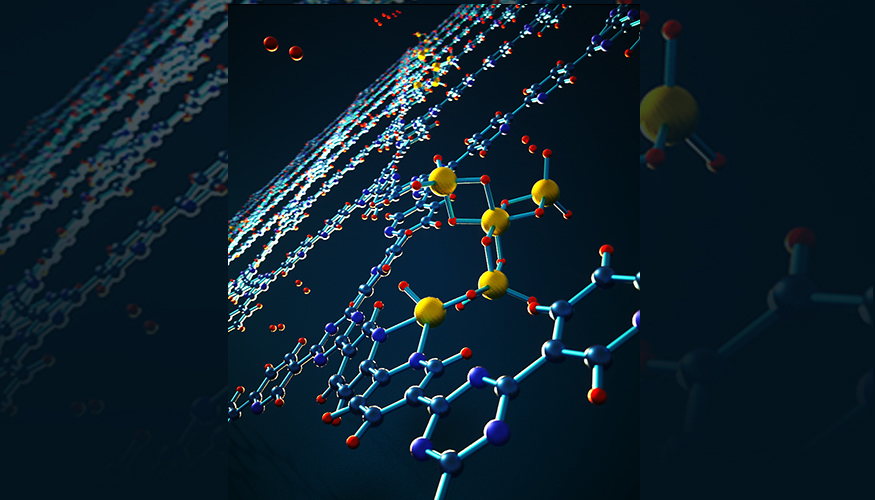
At room temperature, aluminum hydride is a metastable crystalline solid and when it goes through an endothermic reaction it decomposes
to generate aluminum and hydrogen gas. The research team developed a nanoconfined material with improved thermodynamics and placed it within the nanopores of a highly porous bipyridine-functionalized covalent triazine framework, which they called AlH3@CTF-bipyridine.
This configuration made it possible to convert bulk metallic aluminum into alane at 60 degrees Celsius and at a hydrogen pressure of only 700 bar, which compares to 6,900 bar in conventional processes. “This pressure is readily achievable in commercial hydrogen fueling stations, although further improvements are necessary to achieve rapid fueling,” the scientists further explained, noting that current processes used to produce alane are carried out under “extreme conditions.”
Popular content
The academics found that the alane they developed offered more stability. They observed that intrinsically stable radicals and tiny alane clusters interact chemically with the nanopores of the confining framework, which creates thermodynamic conditions that are completely different from those of bulk metallic aluminum. “Nanoconfinement is a really interesting approach for stabilizing metastable hydrogen-storage materials, particularly given the wide palette of potential host materials,” said LLNL materials scientist Brandon Wood.
A full description of the technology can be found in the study Defying Thermodynamics: Stabilization of Alane Within Covalent Triazine Frameworks for Reversible Hydrogen Storage, which was recently published in Angewandte Chemie.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.