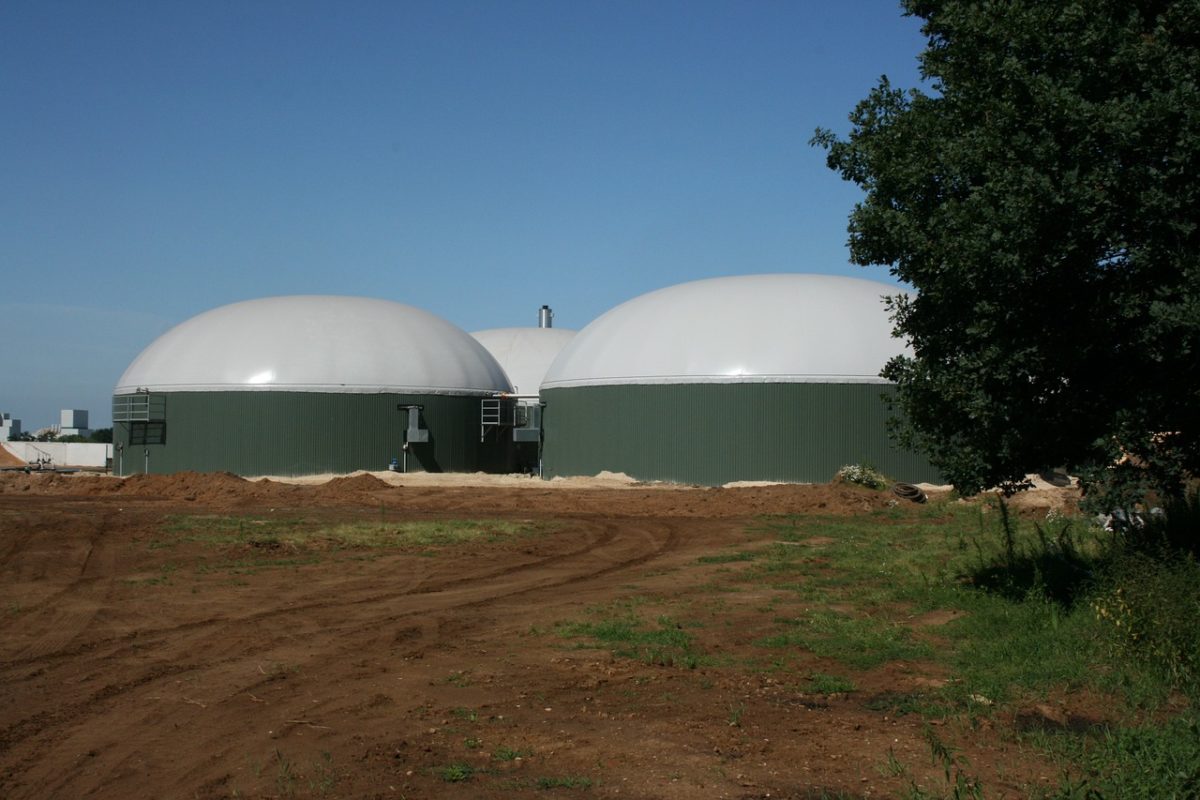
Austria’s Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) and compatriot start-up Rouge H2 Engineering have announced the “world's first” production of high-purity hydrogen from biogas, using a new chemical looping process. The decentralized production of hydrogen occurred at a pressure of up to 100 bar using biogas which included all related impurities. “We [have demonstrated] that a chemical looping system can be integrated into an existing biogas plant,” said Viktor Hacker, from the institute of chemical engineering and environmental technology at TU Graz. “High-purity hydrogen for fuel cells is produced from real biogas; not only in the laboratory but actually on an industrial scale.”
The university said the biogas in question consisted of methane from pig manure; the glycerol phase liquid by-product of biodiesel production; maize silage typically used for cattle feed; and grain residues. “The 10 kW plant diverts about 1% of the biogas flow ([of ]about 30 liters per minute) and mixes it with steam,” TU Graz stated. “The mixture flows into the plant's reactor. There, the biogas is reformed and syngas produced. This gas subsequently reduces iron oxide to iron. Then steam enters the reactor, which reoxidizes the iron back to iron oxide. This releases hydrogen with a purity level of 99.998%.”
The researchers told pv magazine: “Instead of the 1%, the researchers would also be able to channel the entire biogas flow of the biogas plant (about 480 cubic metres per hour) through a correspondingly up-scaled chemical looping plant. This would lead to a 3 MW hydrogen production plant.” Rouge H2 said it is now open to orders from the biogas industry. The researchers forecast a price of €5/kg for the hydrogen produced by their process, but added, pressure-related complexities make the application mostly useful to power tractors and forklift trucks.
The Fortescue Future Industries (FFI), subsidiary of Australian iron ore producer Fortescue Metals Group, has signed a multibillion-pound hydrogen supply deal with British construction equipment maker JCB and Ryze Hydrogen. “JCB and Ryze will purchase 10% of FFI’s global green hydrogen production,” The Australian company said on Sunday. “FFI’s green hydrogen production is anticipated to grow to 15 million tons of GH2 [green hydrogen] per year by 2030, accelerating to 50 million tons per year in the next decade thereafter.” Fortescue said it expects to become the biggest supplier of green hydrogen to the U.K. JCB and Ryze will manage green hydrogen distribution and development of demand in the U.K.
The British government is also trying to send signals promoting corporate partnerships with international players. Last week, Leeds-based Atome Energy signed an agreement with Paraguay’s Itaipu Binational Technology Park relating to the planned location of a 250 MW green hydrogen and ammonia facility. “Atome intends that production will be ramped up from an initial 50 MW unit, commencing [at the] end [of] 2024, with significant potential local end markets,” read a press release re-published by the British government. The U.K. wants to import green and gas-plus carbon-capture-fired blue hydrogen and to promote the nation's technologies abroad. Ramin Navai, the British ambassador to Paraguay, said: “We are very excited about this news. The future production of green hydrogen and ammonia would be a great bilateral achievement, with the U.K. providing its expertise and Paraguay providing its clean energy from Itaipu.”
Fortescue is also making a huge green hydrogen production investment in Argentina. “Fortescue has already started prospecting works in the province of Rio Negro with a view to the production of green hydrogen on an industrial scale, which will require an investment of $8,400 million [€7.26 billion],” wrote the Casa Rosada office of the Argentinian president, after a meeting on the sidelines of this week's COP26 climate summit in Glasgow. That development marked the first major hydrogen announcement made at the global event. According to Argentinian president Alberto Fernández’s office, Rio Negro is expected to reach a production capacity of 2.2 million tons per year by 2030. News about Australian export capacity went hand in hand with local developments as Australian media reported Emerald Coaches, a regional service in central Queensland, has decided to switch its fleet of diesel buses to hydrogen fuel cells, in what local journalists described as an Australian first.
Kazakhstan’s state-owned energy company, KazMunayGas, and German multinational chemical company Linde have signed a memorandum of understanding to jointly develop clean energy projects in the central Asian nation. “The first stage of cooperation will focus on exploring the opportunity of producing hydrogen and ammonia using natural gas as [a] feedstock (blue hydrogen and blue ammonia) and/or water electrolysis (green or blue hydrogen and green or blue ammonia),” read a press release published yesterday, which added the two companies will first proceed with a feasibility study.
The Florida-based Mitsubishi Power Americas storage solutions unit of the Japanese car giant, and Detroit-headquartered natural gas pipeline business, DT Midstream, have signed a strategic joint development agreement (JDA) to promote and develop clean hydrogen projects across the U.S. “The JDA focuses on [the] production, storage, transportation and use of hydrogen and other commodities,” Mitsubishi Power Americas wrote yesterday. “Opportunities include offering hydrogen in liquefied or compressed form for multiple applications such as power generation and transport as well as steelmaking, refining and fertilizer manufacturing.” The partners intend to create inter and intra-state pipelines. Mitsubishi Power has previously announced developments in Utah and North Dakota. “This collaboration will add to the ‘hub and spoke’ hydrogen infrastructure we have been creating with partnerships throughout North America,” said Mitsubishi Power Americas senior VP David Hunt. DT Midstream has approximately 1,200 miles (1,931 kilometers) of transportation pipelines. The companies did not reveal financial commitments or investment figures.
Canada's Hydrogen Optimized has announced the demonstration of the world’s highest-current water electrolyzer since the 1980s. “The operation of a 50,000 ampere RuggedCell unipolar electrolyzer represents a breakthrough in large-scale green hydrogen production technology and a direct pathway toward the commercialization of single electrolysis modules rated up to 100 MW,” the company wrote today.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.


3 comments
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.