How much shade is enough?
Researchers have covered part of a rooftop solar plant with a different numbers of shading cloth layers to measure their power, current, and voltage. They have been able to identify a point after which the value of system current and maximum power is no longer sensitive to shading heaviness.
Monitoring system for vehicle-integrated photovoltaics
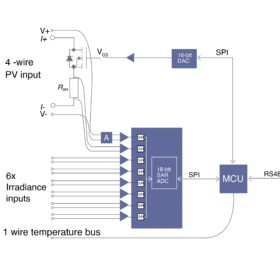
Researchers in Slovenia have built a monitoring system for vehicle-integrated photovoltaics consisting of an IV curve scanner that uses a MOSFET as a voltage-controlled electronic load. The system also utilizes an 18-bit analog-to-digital converter and a microchip microcontroller.
Heliostat field-integrated PVT system supported by organic PCM
Scientists have used stearic acid and a combination of stearic acid and carbon black to increase thermal conductivity in a photovoltaic-thermal system linked to a heliostat field concentrator. From a temperature of 30 C at the inlet, they were able to heat the water to up to 59 C.
New research finds solar module anti-reflective coatings may reduce LCOE by over 2%
Researchers in Morocco have examined the effects of an anti-reflective coating on solar panel performance under desert conditions and have found that it enhanced both the annual performance ratio and the energy yield by 2% and 5.5%, respectively. They have also found it to be durable and able to withstand dry cleaning methods under accelerated testing.
The impact of semi-transparent solar modules on agrivoltaics yield
Researchers have conducted a field study across two growing seasons, growing different kinds of vegetables under three types of modules with 40%, 5%, and 0% transparency. Their work is the first replicated research experiment that evaluates module transparency in an irrigated vegetable field setting.
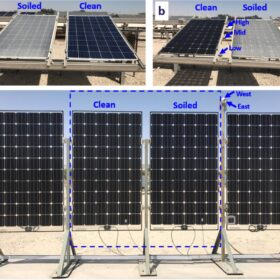
East-west vertical PV as an antidote for soiling in desert climates
New research from Qatar shows that east-west-oriented vertical PV installations can significantly help reduce soiling in desert climates. The scientists found that PV power generation can be up to 9% higher in vertical systems compared to conventional arrays.
Chinese scientists achieve record-breaking 20% efficiency in single-junction organic solar cell
Researchers from the Wuhan University of Technology in China have designed and synthesized a new non-fullerene acceptor for organic solar cells. One of their fabricated devices achieved the highest certified efficiency ever reported for single-junction organic solar cells.
New direct lightning protection design for east-west rooftop PV systems
Scientists in the Emirates have developed a novel lightning mast layout that reportedly eliminates shading effect on PV panels. The proposed approach also addresses earth grid requirements under varying moisture conditions.
PV module cooling tech based on single-channel containing nanofluids
Scientists in Mexico have conceived a new solar module cooling tech that can reportedly improve PV power generation by up to 2%. The system uses nanofluids embedded in an aluminum single-channel attached to the back of the panel.
Novel bifacial flexible PV cell offers 27% efficiency
Scientists have simulated dozens of electron transport layer-free cell structures and have identified the optimal design with a Zr:In2O3 front transparent electrode, a CuSCN hole transport layer, and a NAN rear transparent electrode. They have also optimized its thickness and bandgap.