Fraunhofer ISE achieves 40% efficiency for indoor III-V solar cell
The PV device is based on a indium gallium phosphide absorber with an energy bandgap of 1.9 eV. It is intended for use in autonomous Internet of Things (IoT) applications that operate indoors without an external wired power supply.
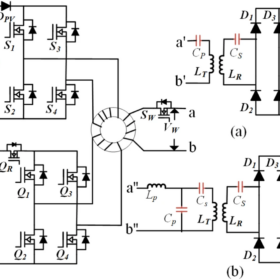
Wireless EV charging based on PV, three-port DC–DC converter
Scientists have developed a wireless charging system for electric vehicles, with a three-port DC–DC converter at its core. They have simulated the system and tested a prototype in their lab and have found it achieved an improved efficiency of 88%.
Solar myths and misconceptions
In a new monthly column for pv magazine, the International Solar Energy Society (ISES) debunks old and new urban legends about solar energy.
ClearVue BIPV solution achieves 2.6-year payback in Hong Kong trial
ClearVue Technologies says its solar facade solutions, that combine the company’s solar glazing units into a fully integrated energy generating building envelope, have achieved a payback period of less than three years in a Hong Kong government trial.
Chinese PV Industry Brief: Tongwei, Longi, JA Solar announce H1 losses
Tongwei, Longi, and JA Solar have predicted steep losses for the first half of 2025, as persistent oversupply and falling solar module prices continue to pressure margins across China’s PV manufacturing sector.
Chinese scientists build copper indium sulfide solar cell with 10.44% efficiency
Copper indium sulfide (CuInS2) are still far from reaching commercial maturity but new titanium dioxide nanorod arrays can reportedly improve their light trapping, charge separation, and carrier collection.
US launches national security probe into polysilicon imports
The US Department of Commerce (DoC) says it will investigate the potential for export restrictions by foreign countries, as well as their ability to “weaponize” their control over supplies of polysilicon.
Precise backside irradiance modeling for bifacial PV is often unnecessary
A European research group has developed a new “empirical” method for measuring the backside irradiance of bifacial PV system. The proposed approach was tested across several European locations and it was found to enable annual performance calculations with a fixed backside irradiance share value.
Using photoluminescence, implied open-circuit voltage imaging for perovskite solar cell field testing
To evaluate the outdoor performance and stability of perovskite solar cells using contactless and noninvasive methods, an Australian and Chinese research team found a way to use photoluminescence imaging as well as demonstrating a proof of concept for implied open-circuit voltage (iVOC) imaging. Their research relied on cost-effective equipment that operates under direct sunlight.
Photovoltaics for cargo ships
Wattlab has installed a PV system capable of delivering up to 35 kW to a cargo ship’s high-voltage propulsion system, allowing it to temporarily replace one of four diesel generators under optimal conditions.