Scientists analyze seasonal performance of rooftop, vertical PV in the Arctic
New research from Finland shows that the best season for rooftop PV generation in the Arctic is spring, and that the best tilt angle for rooftop systems is 28 degrees. It also showed that vertical PV installations perform better in winter.
The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen buses less efficient than battery models
Italian researchers have compared the performance of hydrogen and electric buses in northern Italy, while DNV has released its guidelines to validate claims related to low-carbon renewable hydrogen and ammonia attributes.
Australian coal plant tests iron flow batteries
Energy Storage Industries is delivering 1 MW/10 MWh of flow battery storage to the Stanwell Power Station in the Australian state of Queensland. The flow batteries are part of a new government-run clean energy testing “hub,” featuring hydrogen and additional workforce training programs.
Solar for wildfire detection
Dryad Networks has developed an AI-powered sensor to detect wildfires and notify first responders.
PV cell technology trends
Ongoing innovation in PV cell technology will have major impacts as solar is deployed at a “multi-terawatt scale” over the next two decades, according to a global team of scientists.
New control technique for microgrid-connected PV systems
An international research group has applied for the first time integral backstepping control (IBC) as a control strategy for PV systems connected to microgrids. Through a series of simulations, the scientists found the new approach can provide better results than classic backstepping control (BC) and other techniques.
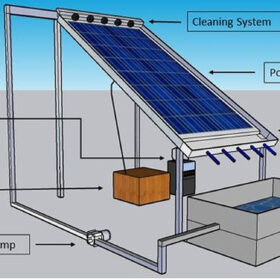
Water-based solar module cleaning tech for rooftop PV
Scientists in Pakistan developed a new cleaning system that reportedly not only reduces power losses caused by soiling but is also able to increase PV module performance by reducing its temperature. It could be applied to both residential and commercial PV systems.
Lochinvar unveils heat pump to supply hot water at up to 70 C
Lochinvar has developed a heat pump with a hot water supply of up to 70 C, with a coefficient of performance (COP) of 5.5. The system is entirely cascadable, offering outputs ranging from 88 kW to 880 kW. It also includes 455 liters of hot water storage capacity and uses propane (R290) as a refrigerant.
Jaguar building large-scale storage system with second-life EV batteries
Jaguar Land Rover and Wykes Engineering are building a 2.5 MWh storage system with electric-vehicle batteries taken from Jaguar I-PACE cars. The large-scale system will store wind and solar at an undisclosed location in the United Kingdom.
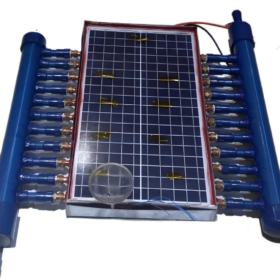
Photovoltaic-thermal panel based on twisted absorber tubes, nanoparticle-enhanced PCM
Developed by scientists in Malaysia, the new PVT system is based on a nanoparticle-enhanced phase change material (Nano-PCM) and twisted absorber tubes. The system consists of a 30 W photovoltaic module, absorber tubes attached to the back of the panel via enhanced silicone glue bond, and a PCM container surrounding the tubes.