Ever heard of photovoltachromics, the new tech for solar windows?
Researchers in China have developed a smart solar window tech based on a photovoltachromic device that is able to achieve a high pristine transmittance and to be self-adaptable to control indoor brightness and temperature. The device was assembled via a full solution process in an architecture incorporating glass, a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) layer, a perovskite-based PV cell, an electrochromic gel, another FTO layer, and glass.
Multi-day iron-air batteries reach commercialization
US-based startup Form Energy has secured $200 million Series D funding for the development of what is being called a breakthrough in energy storage.
Kaco unveils new single-phase string inverter
The blueplanet NX1 M2 series of inverters have an output between 3 and 5 kVa and an efficiency of 97.5%, and are designed for residential rooftop PV systems.
Zinc-iron redox flow battery with zero dendrite growth
Scientists in India fabricated a redox flow battery based on zinc and iron that showed strong storage characteristics and no signs of degradation over 30 charge-discharge cycles. The battery also showed no signs of dendrite formation, overcoming one of the key hurdles for redox-flow batteries based on these low-cost, abundant materials.
Novel plant design for agrivoltaics
Developed by Chinese researchers, the novel design methodology consists of utilizing metal brackets as mounting structures, conventional solar panels, and a grooved glass plate placed between the solar panels. According to its creators, it ensures a farmer’s average income increases by 5.14 times, including the solar power generation business. A system built with this approach should cost around €715 per kW installed.
Sandia researchers develop new grid-scale energy storage battery
The battery operates at 230 degrees Fahrenheit, opening what researchers said could be “a whole cascading cost savings” including everything from less expensive materials to less insulation.
Four-terminal heterojunction perovskite tandem solar cell with 30.09% efficiency
Developed by a Vietnamese-Korean research group, the complex PV device was built with a bottom bifacial crystalline silicon perovskite-filtered heterojunction sub-cell that is able to absorb all solar spectra in the short-wavelength range.
Cutting Europe‘s energy costs through interconnection
A new study from Stanford University professor Mark Jacobson models energy grids powered by 100% wind, water and sunlight across Western Europe. The study finds that in such a scenario, increased interconnection between countries would lead to lower energy costs and better grid stability, as well as a hedge against sudden loss of supply due to extreme weather or other events.
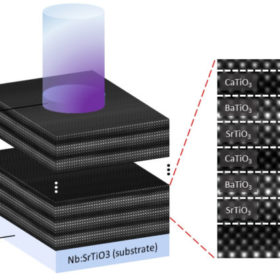
Crystal arrangement results in 1,000x more power from ferroelectric solar cells
German researchers developed a lattice arrangement of three different layers of ferroelectric crystals that created a powerful photovoltaic effect.
The Hydrogen Stream: More hydrogen for the port of Rotterdam
Chiyoda Corporation and Mitsubishi Corporation to conduct a joint feasibility study for a commercial-scale import of hydrogen from overseas sources to one terminal in the port of Rotterdam. Furthermore, the UK government said it wants to produce produce hydrogen from nuclear and Japan’s automotive manufacturer Toyota Motor is looking into geothermal potential for hydrogen production.