South Korea tests photovoltaics on railroad noise barriers
Land-scarce South Korea is currently hosting a series of initiatives aimed at deploying solar on unused surfaces. The latest development comes from the city of Suncheon, which will test several photovoltaic railroad noise barriers based on bifacial PV modules.
South Korea’s first renewables-linked PPA
Korean beauty products supplier Amorepacific has agreed to buy electricity from 5MW of renewables operated by LNG provider SK E&S. The 20-year deal is South Korea’s first step into unsubsidized renewable energy development.
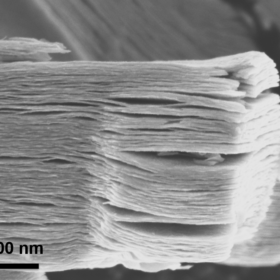
Solar cells based on 2D carbides, nitrides
Researchers from Qatar and South Korea have studied the potential of solar cells based on 2D MXenes materials. They said that titanium carbide MXene (Ti3C2Tx) is the most promising material in the MXene family for PV applications.
PV-powered filling/recharging station for all kind of vehicles, including EVs and fuel cell cars
Built by Korean oil provider SK Energy and the Seoul Metropolitan Government, the “Energy Super Station” is equipped with 20kW of solar panels and 300kW of fuel cell stacks. It can refuel conventional combustion vehicles as well as electric vehicles and fuel cell cars.
The Hydrogen Stream: Airbus plans flight test with direct combustion engine fueled by hydrogen
Elsewhere, Chinese researchers have synthesized ultrafine Pd100-xCux nanodot-modified TiO2 photocatalysts that display optimized energy barrier for interfacial hydrogen desertion, which reportedly exhibits excellent H2-evolution activity and stability, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has presented its plans to establish the Takasago Hydrogen Park, calling it the world’s first center for validation of hydrogen-related technologies, from hydrogen production to power generation.
LG exits solar module business
The Korean manufacturer said its solar module business will be closed by the end of June. It blamed uncertainties in the global solar industry for its decision.
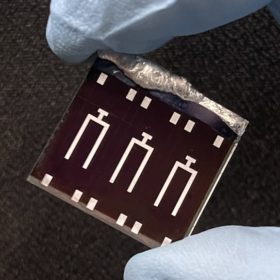
CISSe solar cell with record-breaking efficiency of 14.4%
Korean researchers have built a CISSe solar cell that can be used as a bottom cell for applications in tandem cells with a top cell based on perovskite. In the manufacturing process, they replaced the vacuum technology with air annealing and the result was a record-breaking efficiency combined with potential lower production costs.
Hanwha Q Cells launches 590W solar module with 21.7% efficiency
The Q.Peak Duo XL-G11.3 panel is currently the largest and most powerful panel produced by the Korea-based manufacturer. It features a temperature coefficient of -0.34% per degree Celsius and comes with a 25-year linear performance warranty.
South Korea’s Kepco to deploy 100MW of highway PV
Korea Electric Power Corp. plans to build solar on highways in two 20MW stages, followed by a third phase, under a government program to facilitate the development of energy-independent roads.
Hanwha Q Cells begins selling its solar panels based on M6 wafers in Europe
The Q Peak Duo XL-G10 panel series is based on monocrystalline ‘Qantum’ half cells and is the company’s first panel relying on M6 wafers.