Long-duration storage solution based on saltwater
Developed by Dutch start-up AquaBattery, the storage technology is claimed to independently amend power and energy capacity. The battery system utilizes three storage tanks, one with fresh water, one with concentrated salt water and one with diluted salt water, and also relies on membrane stacks.
New method for long-term prediction of renewables generation in Europe
Developed by scientists in Spain, the new methodology is claimed to be capable of mitigating energy crises in Europe through climate predictions.
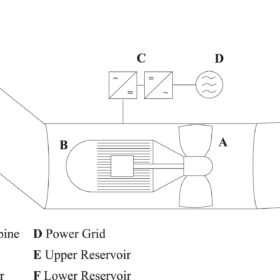
Pushing the boundaries of low-head pumped hydro storage
Two different studies have highlighted the potential and challenges of low-head pumped hydro storage (PHS), which has so far never been implemented in real projects. Different main areas were identified for future research and an interesting levelized cost of storage was indicated for certain project configurations.
Zinc-ion battery for residential applications
Developed by Canadian start-up Salient Energy, the zinc-ion battery has a rated capacity of 60 Ah, a nominal voltage of 1.3 V, and a volumetric energy density of 100 Wh/L. The device measures 26cmx24cmx1.2cm and weighs in at 1.3 kg
Colombia’s Minister of Mines and Energy discusses the state of solar at BNEF Summit
pv magazine publisher, Eckhart Gouras, interviewed Diego Mesa, the Colombian Minister of Mines and Energy at the BNEF Summit in New York. Mesa recounted the history of solar PV adoption in his country and provided details on the most recent developments, including the construction of Colombia’s largest solar park by Italian group Enel and the first large scale battery project by Canadian Solar.
Panasonic combines fuel cells, batteries, PV to power factory in Japan
Japan’s Panasonic claims its new pilot solar-plus-hydrogen facility marks the first attempt to create a factory powered by 100% renewables, via the full-scale use of hydrogen.
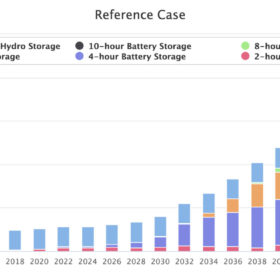
NREL’s storage projections for 2050
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) final report on the future of storage presents “key learnings” from a series of six in-depth studies.
The mobility rEVolution: Honda ups the ante on EVs, solid state batteries
In other news, further Covid-19 lockdowns in China continue to negatively impact the EV battery supply chain and broader industry, Porsche is testing V2G capabilities, and Israeli startup Electreon announces extension of its wireless dynamic EV charging project in Sweden.
Neoen, AGL sign Australia’s first grid-scale virtual battery contract
French renewable energy developer Neoen has signed a seven-year agreement with Australian utility AGL to provide 70 MW/140 MWh of virtual battery capacity in New South Wales.
US start-up develops polymer-based batteries for stationary storage
Developed by an MIT spin-off, the device is based on a standard, two-electrode electrochemical cell containing conductive polymers, a carbon-graphene hybrid, and a non-flammable liquid electrolyte. The battery cells were tested to perform for 12,000 cycles at 100% depth of discharge.