Cathode formation issue could drive improvements in battery resiliency
Researchers at the Argonne National Laboratory have discovered a degenerative effect in the creation of cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries that could have significant impacts on the performance of sodium-ion batteries.
Developing better behind-the-meter energy storage
NREL researchers work on developing high energy density cells to advance stationary storage.
Ricoh launches mini hydropower system for remote locations, usable with solar-plus-storage
The pico-hydro generation system can be used with factory drainage systems and irrigation canals. According to the manufacturer, it is made with 3D-printed sustainable materials and is able to generate electricity even with a small stream of water. Solar and storage may be linked to the system to ensure stable power supply.
Energy storage installations set new records in the U.S. despite supply chain issues
Wood Mackenzie estimates that the US energy storage market broke records in Q4 2021, installing 1,613MW / 4727 MWh.
Australia’s AGL builds storage portfolio
Australia’s largest power utility, AGL, says it has received approval for a 200 MW/800 MWh grid scale battery to be developed at the site of its coal-fired Loy Yang power station in Victoria’s Latrobe Valley.
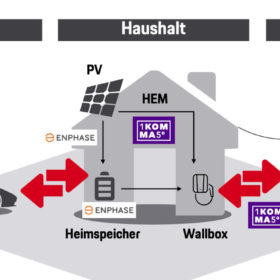
1Komma5°, Enphase plan European virtual power plant relying on solar, storage, heat pumps and EV recharging
Through a strategic partnership, the two companies want to equip 1.5 million buildings in Europe with photovoltaics, storage systems, recharging solutions for electric vehicles, and heat pumps by 2030.
Latent heat thermophotovoltaic battery for renewables storage
Developed by researchers in Spain, the battery uses renewable electricity to melt low-cost metals such as silicon or ferrosilicon alloys to produce and store latent heat, which is in turn used by a thermophovoltaic generator to produce power. According to its creators, the device may store electricity at a cost of €10 per kilowatt-hour for a 10MWh system.
Above-bandgap light tech to improve performance of lithium-ion batteries, fuel cells
A US-German research group has used above-bandgap light to improve ion mobility in ceramic materials used in lithium-ion batteries and fuel cells. It found that the grain boundary conductance of gadolinium-doped cerium oxide, which is a ceramic used as a solid-state electrolyte in fuel cells, can be improved by a factor of approximately 3.5 at 250 degrees Celsius, by applying the proposed light technique.
Tesla opens gigafactory in Germany
The first Model Y electric cars have rolled off the assembly line at the US electric car manufacturer’s first European factory.
The case for aqueous zinc-ion batteries
Scientists in Germany have identified the main challenges that are preventing aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) from becoming a mainstream storage technology for power grid applications. According to their analysis, the two main hurdles that must be overcome in future research are the increase of the specific energy of the full Zn-ion cell and the prevention of the parasitic hydrogen evolution reaction occurring during the Zn electrodeposition step.