The Hydrogen Stream: Steam-based tech to produce 100 g of hydrogen from 1 kg of biomass
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) developed a two-phase hydrogen production technology that is capable of using steam to produce hydrogen from biomass. Furthermore, an Indian-Norwegian consortium is developing green ammonia in Oman, Toshiba is starting research on hydrogen production from geothermal energy, and Thyssengas is selecting personnel for the conversion of around 20% of its gas network.
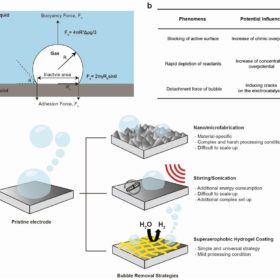
The Hydrogen Stream: New hydrogel for bubble detachment in hydrogen production
South Korean researchers have published a new study on the use of hydrogel to remove gas bubbles in hydrogen production, while Shell has revealed that it will continue with its hydrogen investments in the Netherlands, Vestas, meanwhile, said it will launch a pilot project to use hydrogen in a crew transfer vessel.
Acme to build 1.5 GW green hydrogen project in India
Indian developer Acme will set up a green hydrogen and ammonia project in Tamil Nadu with 1.5 GW of electrolysis capacity and 1.1 million tons of ammonia synthesis, powered by a 5 GW solar plant.
EPC tender for solar-powered hydrogen project in Portugal
Hyperion Renewables launched an EPC tender for its Green H2 Setúbal Project back in March. Seven companies are now competing to build a plant with a green hydrogen production capacity of 135 kg (1,500 Nm3) per hour. The plant will be fed by 12 MW of solar PV.
The Hydrogen Stream: Romania calls for green hydrogen projects
Romania has unveiled a state aid scheme to support investments in the production of hydrogen powered by solar, hydro and wind, while Air Products and Gunvor have agreed to build a hydrogen import terminal in Rotterdam.
The Hydrogen Stream: Volvo starts testing fuel cell electric trucks
Volvo said it will offer fuel cell electric trucks by the second half of the decade, while an airport in northern Japan has started working on a feasibility study for local hydrogen production. Uruguay, meanwhile, has presented a new hydrogen strategy.
Hydrogen generation from organic waste, non-recyclable plastic
US-based H2 Industries plans to produce hydrogen from organic waste and non-recyclable plastic. pv magazine recently spoke with its executive president, Michael Stusch, about the main technologies behind the project.
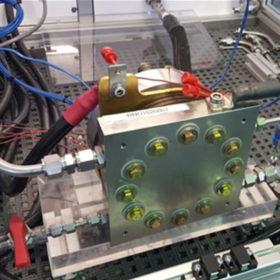
Novel stack design for PEM electrolyzers promises lower production costs
Researchers in Germany have built bipolar plates for electrolyzer stacks without using titanium, which they claim may further reduce green hydrogen costs. They used coated stainless steel and niobium for the stack coating and found these new materials do not affect electrolyzer performance.
The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen system for marine vessels
DNV approved HAV Group’s hydrogen-based energy system for cruise vessels, Rolls-Royce agreed to sell hydrogen-powered mtu fuel cell solutions in Germany, and the Mauritanian government signed a deal with CWP to develop a 30 GW green hydrogen project.
The Hydrogen Stream: World’s first hydrogen-powered towboat
Shipbuilder Hermann Barthel has developed the world’s first push boat to combine battery-electric propulsion with hydrogen and fuel cell technology. Iberdrola and Fertiberia, meanwhile, have commissioned Europe’s largest green hydrogen production plant.