Toyota unveils 8.7 kWh battery for residential applications
The battery has a rated output of 5.5 kW and can be installed in outdoor environments. It is equipped with a hybrid power conditioner, a DC-to-DC converter, and a vehicle power supply adapter with a maximum output of 1.1 kWh.
Achieving a zero-carbon grid with virtual power plants
Jigar Shah reflects on the challenges that come with achieving a zero-carbon electric grid and how virtual power plants (VPPs) can turn those challenges into opportunities for all Americans.
Redflow announces integration with US inverter company
Australian redox-flow battery specialist Redflow has upped the ante on its plans to expand into the US market, announcing that it has completed testing to pave the way for its battery energy storage system to be used in conjunction with hybrid inverters manufactured by US solar engineering company Sol-Ark.
The Hydrogen Stream: World’s first hydrogen-powered towboat
Shipbuilder Hermann Barthel has developed the world’s first push boat to combine battery-electric propulsion with hydrogen and fuel cell technology. Iberdrola and Fertiberia, meanwhile, have commissioned Europe’s largest green hydrogen production plant.
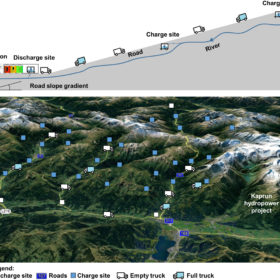
Storing hydropower via regenerative braking in electric trucks
An international research team has proposed the use of water from high-altitude rivers and regenerative braking in electric trucks to store electricity for reuse in power networks, or for transport purposes.
Tesla rallies Powerwall owners to show how they can help Texas grid
In Texas, where batteries cannot send power to the grid, Tesla has filed a request for a rule change and has called on Powerwall owners to form a virtual power plant.
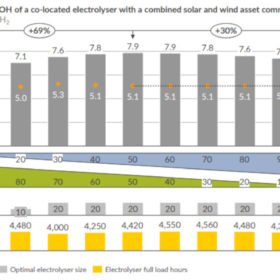
Green hydrogen price may drop to €5 kg by 2025
Aurora Energy Research says in a new report that maximum green hydrogen project profitability could be achieved when solar and wind power plants are combined with electrolyzers.
China’s first salt cavern for compressed air energy storage goes online
Huaneng Group has finished building a 300 MWh storage project in Changzhou, in China’s Jiangsu province. The state-owned company has already started operating the facility, which is situated in a salt cavern.
Solar-plus-storage vs. wind-plus-storage
US scientists have come up with an analytical way to evaluate the costs and net value of different configurations of large-scale wind and solar projects paired with battery storage. They identified six trends in the US electricity market and found that their framework is aligned with current commercial practices.
British developer gets green light for 200 MW battery
The Heysham site is intended to reduce curtailment from half a dozen offshore wind farms and to replace local grid services which will be lost when two nearby nuclear reactors are powered down.