Work begins on green hydrogen storage cavern in Sweden
Vattenfall, SSAB and LKAB are building a rock cavern storage facility in a coastal city in northern Sweden. The 100-cubic-meter facility will be built 30 meters below ground and will begin storing green hydrogen next year.
Solar PV driving green hydrogen to undercut gas, says BloombergNEF
BloombergNEF has shown that solar PV is the key driver of declining green hydrogen costs. The forecast shows costs falling by 85% by 2050, undercutting natural gas and blue and gray hydrogen production.
The Hydrogen Stream: Projects move forward in China, Japan, Australia and across several European countries
Sinopec wants to build 1,000 hydrogen refueling stations by 2025. Ways2H is building a facility in the Tokyo area that will convert daily 1 ton of dried sewage sludge into 40-50 kilograms of hydrogen for fuel cell mobility and power generation. Ørsted wants to deploy two renewable hydrogen production facilities for a total of 1 GW by 2030. Wacker Chemie is planning to produce green hydrogen and renewable methanol at its German site.
Australian scientists achieve breakthrough with renewably powered carbon capture
Australian scientists have achieved a new breakthrough in carbon capture and storage. Their novel electrochemical process can store carbon dioxide in water with the power of solar or wind, while also producing by-products such as green hydrogen and calcium carbonate – perhaps the key to decarbonizing the cement industry.
The Hydrogen Stream: Siemens targets $1.50/kg by 2025, BP and Saudi Aramco bet on blue hydrogen
The German company expects to roll out its in-house proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis technology to implement a gigawatt production of electrolyzers. BP partners with UK gas distributor Northern Gas Networks (NGN) to develop blue hydrogen and Saudi Aramco teams up with Hyundai Heavy Industries to do the same. Italy’s Snam wants to build hydrogen projects in the United Arab Emirates.
Australia’s first hydrogen refueling station opens in Canberra
Neoen and ActewAGL have opened Australia’s first hydrogen vehicle-refueling station in Canberra. It will cater to the state government’s new fleet of Hyundai Nexo hydrogen cars.
EV recharging station powered by solar, hydrogen
The recharging station was designed by French automation group Sirea. It is powered by a solar carport and a small electrolyzer.
Incentives crucial to avoid green, blue, and even purple hydrogen fading to grey
An Anglo-German report has suggested the environmentally-friendly desire to use only clean power to produce hydrogen, outlined by nations such as Germany, could end up being more emissions-heavy than the more pragmatic embrace of blue hydrogen under consideration in the U.K.
Chile wants to export green hydrogen to Port of Rotterdam
The Chilean Minister of Energy and Mining has announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding to export green hydrogen to the Port of Rotterdam. The deal adds to the one signed with Singapore in early March to identify the best routes to reach Asian markets.
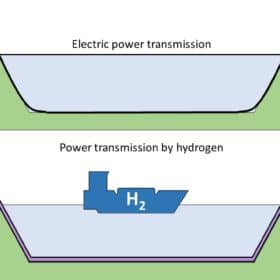
Hydrogen shipping vs submarine cables
Hydrogen transportation and submarine power lines have been compared by an international research team to find out which may be the cheapest option to connect for energy exchange regions separated by the sea. According to their findings, the hydrogen shipping alternative does not present very good prospects of applicability in the future, unless some disruptive technological breakthroughs are made. What makes compressed and liquified hydrogen ships still attractive, however, is that they can export energy almost anywhere, and that electrolysis and liquefaction plants are relatively easy to expand compared to marine cables.