NREL-led consortium releases PV reliability forecasting tools
The Durable Module Materials consortium (DuraMAT) announced in its latest annual report the availability of new PV forecasting tools, and new research results towards the goal of more reliable PV modules.
US, Canada ramp up solar glass plans
With PV module capacity ramping up, glass suppliers have been investing in new solar glass production capacity. As in India and China, new facilities are popping up in North America, with unique twists to ensure competitiveness, such as using recycled material.
NREL updates interactive chart of solar cell efficiency
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has updated its research cell efficiency chart for a range of PV technologies.
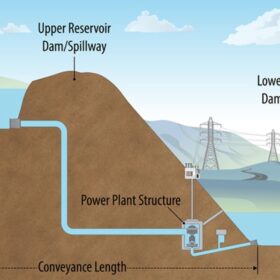
NREL releases online tool to estimate pumped hydro storage costs
The US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has released a cost-estimation tool for new closed-loop pumped storage hydropower (PSH) plants in the United States. The tool allows operators to select from a range of system characteristics and account for factors such as local geology, labor rates and inflation.
NREL updates online tool with data for Africa, Eastern Europe, Middle East
The US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has added a high-resolution solar data set covering Africa, Eastern Europe and the Middle East on its Renewable Energy Data Explorer tool.
Perovskite thin film: Out with the old, in with the new
Silicon-perovskite tandem solar requires optimization of both approaches, and embodies the weaknesses of each. Meanwhile, the use of pure thin-film devices offers a cheaper, simpler, and more sustainable PV solution for the United States.
Has the US caught up with European agrivoltaic deployment?
With so much more agricultural real estate than Europe, the United States is building on the body of research built up across The Pond and rolling out solar panels on farmland at an impressive rate.
Weekend Read: Temper tantrum
Reports of broken module glass with no obvious cause have begun to crop up at large PV projects. Module design, glass manufacturing, and interactions in the field between modules and trackers are at play and a clear solution has yet to emerge. Early signs suggest an update to certification standards may be needed.
NREL presents new GaAs solar cell concept with 27% efficiency
The US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has identified a low-cost way to produce high-efficiency III-V solar cells with dynamic hydride vapor phase epitaxy (D-HVPE). The synthesis involved a gallium arsenide (GaAs) solar cell with a gallium indium arsenide phosphide emitter layer.
New opportunities for 4-hour-plus energy storage
Energy storage with more than four hours of duration could assume a key role in integrating renewable energy into the US power grid on the back of a potential shift to net winter demand peaks, says the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).