Panasonic combines fuel cells, batteries, PV to power factory in Japan
Japan’s Panasonic claims its new pilot solar-plus-hydrogen facility marks the first attempt to create a factory powered by 100% renewables, via the full-scale use of hydrogen.
Smarten launches 2.4 kW hybrid PV power conditioning unit for offgrid applications
Smarten has released the Superb 3050 hybrid solar power conditioning unit (PCU) for offgrid applications. The 2.4kW product is priced at INR 19,999 ($260).
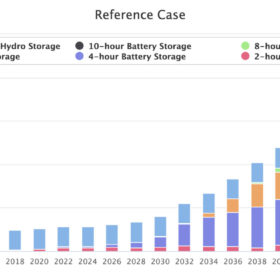
NREL’s storage projections for 2050
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) final report on the future of storage presents “key learnings” from a series of six in-depth studies.
The mobility rEVolution: Honda ups the ante on EVs, solid state batteries
In other news, further Covid-19 lockdowns in China continue to negatively impact the EV battery supply chain and broader industry, Porsche is testing V2G capabilities, and Israeli startup Electreon announces extension of its wireless dynamic EV charging project in Sweden.
Neoen, AGL sign Australia’s first grid-scale virtual battery contract
French renewable energy developer Neoen has signed a seven-year agreement with Australian utility AGL to provide 70 MW/140 MWh of virtual battery capacity in New South Wales.
Brazil’s Cemig launches another wind, solar auction
The Brazilian energy company will award 10-year and 15-year power purchase agreements (PPAs) to projects exceeding 50 MW in size through this new procurement exercise.
Bangladeshi fabrics maker invests in 100 MW solar plant
The solar park will sell power to the Bangladesh Power Development Board at a price of $0.1195/kWh under a 20-year power purchase agreement.
The Hydrogen Stream: Fuel cell engines for stationary power uses
In other news, Airbus and Kawasaki Heavy Industries plan to work together to prepare a hydrogen-fueled ecosystem, while Storgrundet Offshore and Lhyfe want to build a 600 MW hydrogen production plant in Sweden. Furthermore, Canada-based First Hydrogen has identified four industrial sites in the United Kingdom and is advancing discussions with landowners to secure land rights to develop green hydrogen production projects.
Hybrid thermionic-photovoltaic converter for applications in thermal energy storage, waste heat recovery
A Spanish-Italian research group has developed a solid-state thermal-to-electric energy converter based on hybrid thermionic-photovoltaics (TIPV) for different applications. It consists of a three-terminal TIPV device made with a tungsten (W) thermionic cathode, a PV/anode structure made of an indium phosphide (n-InP) anode, and a photovoltaic cell based on indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs).
US start-up develops polymer-based batteries for stationary storage
Developed by an MIT spin-off, the device is based on a standard, two-electrode electrochemical cell containing conductive polymers, a carbon-graphene hybrid, and a non-flammable liquid electrolyte. The battery cells were tested to perform for 12,000 cycles at 100% depth of discharge.