Bifacial CdTe solar cell achieves record power density via film lithography
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and First Solar have used cracked film lithography (CFL) to build a bifacial cadmium telluride solar cell with a power density of 20.3 mW cm−2. They claim the cell has a higher bifacial power density than any polycrystalline absorber currently manufactured at scale.
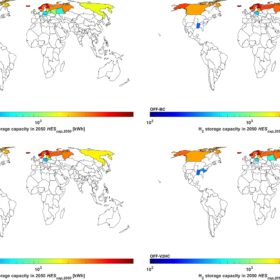
Seasonal hydrogen storage for residential self-consumption
Finnish and German researchers have assessed the role of seasonal hydrogen storage for PV prosumer households with a “least-cost” model at a global level up to 2050. They have found that seasonal hydrogen storage can only be expected in a niche, off-grid market.
‘Natural clay’ additive promises gains in perovskite solar cell efficiency, stability
Scientists in Turkey have demonstrated that sepiolite, a naturally occurring clay substance, can be added to perovskite precursor materials, and form a scaffold layer that can improve the efficiency and stability of the cells. The scientists believe that this substance could be valuable in developing reproducible processes for the production of large-area perovskite solar cells.
Battery hydrogen vs. battery flywheel
Scientists in Italy have looked at how flywheel storage and reversible solid oxide cells could be integrated with lithium-ion batteries in minigrids powered by solar. They found that flywheels combined with batteries could be the cheapest option for power smoothing.
Hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cell for BIPV, bifacial applications
Scientists in South Korea have developed a flexible, transparent solar cell with an average visible transmittance (AVT) of 88.3%. They have also created an n-type rear window layer to optimize bifacial operation.
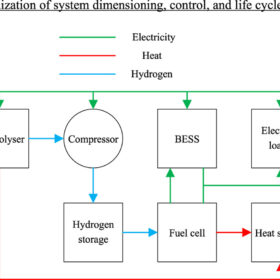
How to combine offgrid PV, heat pumps, and fuel cells in residential complex
Finnish researchers have studied different scenarios to convert a Nordic oil-heated townhouse into a carbon-neutral building. They dimensioned an off-grid PV-powered heat pump system using waste heat recovery from a hydrogen storage system and calculated its life-cycle cost. They concluded that the solution is less profitable than grid-connected systems.
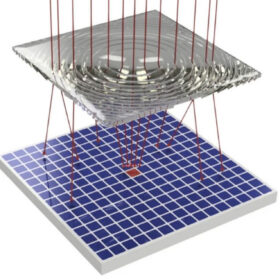
Taiwanese scientists develop high-concentration PV system
Taiwanese researchers have developed a system featuring a 2 × 2 Fresnel lens array and a solar panel made of III-V materials and polycrystalline solar cells, with low light leakage.
Triple junction perovskite solar cell hits 24.3% efficiency
An international research group created a triple-junction perovskite solar cell with an efficiency of 24.3% and a quasi-steady-state efficiency of 23.3%. The prototype cell, which has been independently certified by the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), features rubidium/cesium mixed-cation inorganic perovskites with a bandgap of around 2.0 eV to suppress light-induced phase segregation.
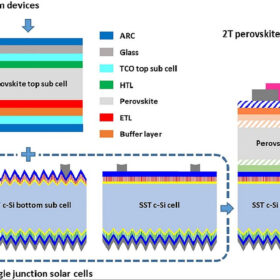
Poly-SiOx solar cell for 4T, 2T perovskite-silicon tandem devices
Scientists in the Netherlands have developed a new crystalline solar cell based on poly-SiOx passivating contacts. The poly-SiOx tech results in a 20% efficiency rating, but 4T tandem perovskite-silicon solar cells based on the poly-SiOx cell can reach an efficiency of 28.1%, and 2T tandem perovskite-silicon devices can hit 23.2%.
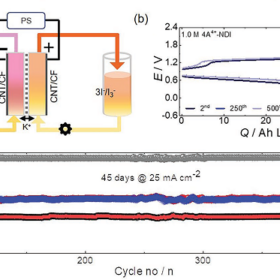
Aqueous redox flow battery based on naphthalene diimide achieves high capacity retention
Scientists in South Korea have developed a highly soluble, stable organic redox-active molecule for use in aqueous redox flow batteries. The newly developed naphthalene diimide (NDI) molecule offered higher storage capacity than existing vanadium devices.