Solar Inventions gets patent for silver-saving configurable current solar cells
Solar Inventions has patented technology that could save between $2 million and $5 million per gigawatt in solar projects, while also raising rated power output. The company has patents in the United States, China and Israel for its cell configuration.
Flexible, roll-to-roll printed perovskite solar cell hits 16.7% efficiency
Australian scientists have demonstrated a flexible perovskite solar cell using roll-to-roll compatible “printing” type processes, which could potentially be applied in large-scale manufacturing. Of particular note is the development of a viable roll-to-roll process to deposit the electrode layer, which has thus far been a major challenge. Cells fabricated by the group achieved a maximum efficiency of 16.7%.
Heterojunction solar cells with lower silver consumption via rotary screen printing
Scientists from the Fraunhofer ISE built a bifacial heterojunction solar cell with a power conversion efficiency of 21.7% via rotary screen printing. They used a machine that is able to achieve a cycle time of just 0.6 seconds per solar cell and enables a strong reduction in silver use.
Average silver price expected to drop 1% to $24.80 per ounce this year
According to the Silver Institute, global industrial silver demand is expected to grow 8% this year due to strong demand in all key sectors, including the PV industry.
Novel solar cell architecture to reduce silver costs, improve voltage
Developed by a U.S.-based start-up, the new manufacturing process is claimed to reduce silver consumption and improve solar module performance by up to 3 W. It consists of connecting sub-cells in series within a single cell in order to increase the device voltage and without requiring cells to be physically broken and rewired.
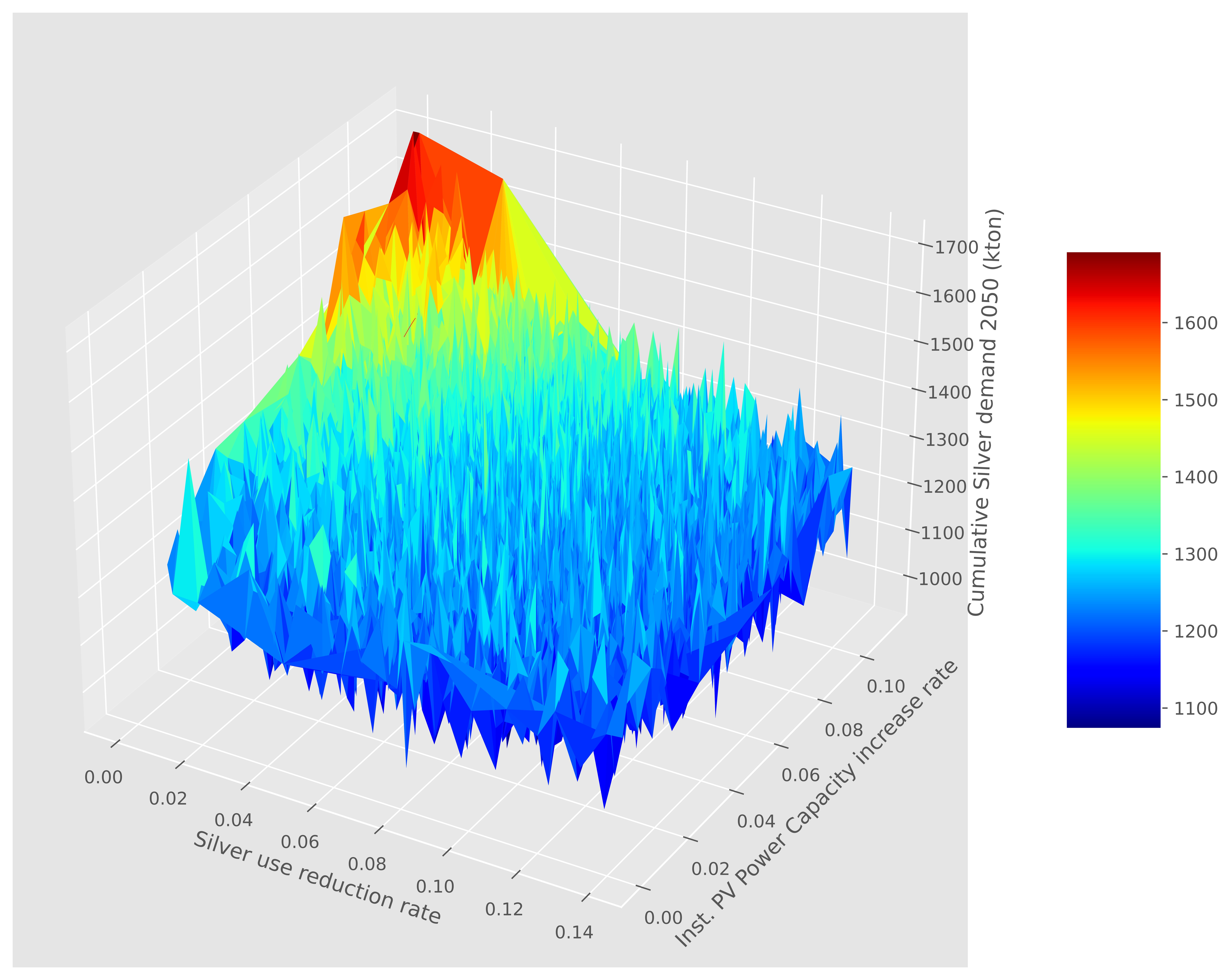
Simulating PV’s silver future
Scientists at Germany’s Fraunhofer ISE developed a model to simulate different setups for screen printing in solar cell metallization. The model provides a comparable ‘screen utility index’ value that can predict the usefulness of different architectures in the printing equipment in relation to the properties of a given silver paste. The approach, says Fraunhofer, will assist the PV industry in reducing the amounts of silver needed in silicon cell manufacturing.
Silver accounts for 10% of PV module costs
The share of silver in the total cost of PV modules has increased by around 5% in recent months, according to US analyst Matthew Watson. He told pv magazine that silver prices are set to rise, adding that the metal will eventually account for an even larger percentage of overall module costs.
Rising prices may push PV industry away from silver
Increasing prices may prompt module manufacturers to find alternatives, or at least reduce silver use in solar cell metallization, according to a recent study. Researcher Samuele Lo Piano, however, told pv magazine silver availability does not represent an issue for large scale PV. Copper-nickel alloys may offer an alternative, he added, but there could be a long wait for them to be viable.
Silver prices expected to rise by 11% this year
Silver demand for PV production worldwide is forecast to grow to 105 million ounces this year, as overall demand hits an eight-year high. Prices for the precious metal could reach a seven-year high of $30.00 per ounce this year but, according to the Silver Institute, this level is still far away from any critical threshold that would make silver supply for the solar industry problematic.
Copper metallization process reaches pilot production in Germany
Scientists led by staff from Germany’s Fraunhofer ISE have demonstrated a new laser printing process in pilot production, which could replace silver paste and screen printing in solar cell manufacturing. The system is said to offer much more flexibility in the layout of contact fingers on the cell surface and a wider choice of metallization materials.